CMS-Flow:Equilibrium Bed load plus AD Suspended load: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (7 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Equilibrium Bed load plus Advection-Diffusion Suspened load Transport model == | == Equilibrium Bed load plus Advection-Diffusion Suspened load Transport model == | ||
| Line 21: | Line 22: | ||
== Pick-up and Deposition Rate == | == Pick-up and Deposition Rate == | ||
The AD model calculates the bed level change due to suspended load from | The AD model calculates the bed level change due to suspended load from the difference between pick-up rate and deposition rate in | ||
the difference between pick-up rate and deposition rate in Equation | |||
pick-up rate and the deposition rate are also applied as the bottom boundary condition in Equation | {{Equation|<math> | ||
{{Equation|<math>P = \left. -\epsilon \frac{\partial c}{\partial z}\right |_{z=a} = c_a w_f</math>| | \frac{\partial h}{\partial t} = \frac{1}{1-p}\left(\frac{\partial q_{bx}}{\partial x} + \frac{\partial q_{by}}{\partial y} + P - D \right)</math>|3}} | ||
where q<sub>bx</sub> = bed load transport rate parallel to the x-axis, q<sub>by</sub> = bed load transport | |||
rate parallel to the y-axis, and p = porosity of sediment. | |||
The pick-up rate and the deposition rate are also applied as the bottom boundary condition in | |||
{{Equation|<math> | |||
\frac{\partial (Cd)}{\partial t}+ \frac{\partial(Cq_x )}{\partial x} + \frac{\partial(Cq_y )}{\partial y} = \frac{\partial}{\partial x} \left(K_x d\frac{\partial C}{\partial x} \right) + \frac{\partial}{\partial y} \left(K_y d\frac{\partial C}{\partial y} \right) + P - D | |||
</math>|4}} | |||
in which | |||
:C = depth-averaged sediment concentration | |||
:d = total depth (= h+η) | |||
:h = still-water depth | |||
:η = deviation of the water-surface elevation from the still-water level | |||
:t = time | |||
:q<sub>x</sub> = flow per unit width parallel to the x-axis (= ud) | |||
:q<sub>y</sub> = flow per unit width parallel to the y-axis (= vd) | |||
:u = depth-averaged current velocity parallel to the x-axis | |||
:v = depth-averaged current velocity parallel to the y-axis | |||
:K<sub>x</sub> = sediment diffusion coefficient for the x direction | |||
:K<sub>y</sub> = sediment diffusion coefficient for the y direction | |||
:P = sediment pick-up rate (upward sediment flux) | |||
:D = sediment deposition rate (downward sediment flux) | |||
The boundary conditions are specified at an arbitrary level <math>\alpha</math> above the mean bed level: | |||
{{Equation|<math>P = \left. -\epsilon \frac{\partial c}{\partial z}\right |_{z=a} = c_a w_f</math>|5}} | |||
{{Equation|<math> D = c_0 w_f</math>| | {{Equation|<math> D = c_0 w_f</math>|6}} | ||
where c = equilibrium concentration of suspended sediment at a given elevation, and z = vertical coordinate. Both c<sub>a</sub> and c<sub>0</sub> are reference concentrations defined at z = a. Because the upward flux of sediment depends on the bed shear stress, c<sub>a</sub> is determined from the bed shear stress calculated from the local hydrodynamic conditions. Representation of c<sub>a</sub> within CMS-M2D is dependent on selection of either the van Rijn or Lund-CIRP models. The downward sediment flux depends on the concentration in the upper water column; therefore, c<sub>0</sub> is specified from solution of Equation | where c = equilibrium concentration of suspended sediment at a given elevation, and z = vertical coordinate. Both c<sub>a</sub> and c<sub>0</sub> are reference concentrations defined at z = a. Because the upward flux of sediment depends on the bed shear stress, c<sub>a</sub> is determined from the bed shear stress calculated from the local hydrodynamic conditions. Representation of c<sub>a</sub> within CMS-M2D is dependent on selection of either the van Rijn or Lund-CIRP models. The downward sediment flux depends on the concentration in the upper water column; therefore, c<sub>0</sub> is specified from solution of Equation 4. | ||
Assuming that the suspended concentration is in equilibrium <math>(\partial c/\partial t = 0, \partial u/\partial x = \partial v/\partial y = 0, \partial c/\partial x = \partial c/\partial y = 0)</math> , then the basic equation for suspended sediment concentration can be written: | Assuming that the suspended concentration is in equilibrium <math>(\partial c/\partial t = 0, \partial u/\partial x = \partial v/\partial y = 0, \partial c/\partial x = \partial c/\partial y = 0)</math> , then the basic equation for suspended sediment concentration can be written: | ||
{{Equation|<math> cw_f + \epsilon \frac{\partial c}{\partial z} = 0 </math>| | {{Equation|<math> cw_f + \epsilon \frac{\partial c}{\partial z} = 0 </math>|7}} | ||
This equation can be solved analytically by applying an appropriate mixing | This equation can be solved analytically by applying an appropriate mixing | ||
coefficient <math>\epsilon</math>, and the vertical profile of suspended concentration is obtained in the following form: | coefficient <math>\epsilon</math>, and the vertical profile of suspended concentration is obtained in the following form: | ||
{{Equation|<math> c(z) = c_0 F(z)</math>| | {{Equation|<math> c(z) = c_0 F(z)</math>|8}} | ||
where F(z) is a function of the vertical concentration distribution. The | where F(z) is a function of the vertical concentration distribution. The | ||
relationship between the reference concentration c<sub>0</sub> and the depth-averaged concentration C is: | relationship between the reference concentration c<sub>0</sub> and the depth-averaged concentration C is: | ||
{{Equation|<math> C = \frac {1}{d-a}\int^d _a c_0F(z)dz</math>| | {{Equation|<math> C = \frac {1}{d-a}\int^d _a c_0F(z)dz</math>|9}} | ||
Thus, c<sub>0</sub> may be written in the following form by introducing a conversion function <math>\beta_d</math>: | Thus, c<sub>0</sub> may be written in the following form by introducing a conversion function <math>\beta_d</math>: | ||
{{Equation|<math> c_0 = \frac {C}{\frac{1}{d-a}\int^d _a F(z)dz} = \frac{C}{\beta_d}</math>| | {{Equation|<math> c_0 = \frac {C}{\frac{1}{d-a}\int^d _a F(z)dz} = \frac{C}{\beta_d}</math>|10}} | ||
| Line 52: | Line 81: | ||
the two types of reference concentration: | the two types of reference concentration: | ||
{{Equation|<math> P - D = (c_a - c_0 ) w_f</math>| | {{Equation|<math> P - D = (c_a - c_0 ) w_f</math>|11}} | ||
This equation implies that erosion occurs if c<sub>a</sub> > c<sub>0</sub>, and accretion occurs if c<sub>a</sub> < c<sub>0</sub>. | This equation implies that erosion occurs if c<sub>a</sub> > c<sub>0</sub>, and accretion occurs if c<sub>a</sub> < c<sub>0</sub>. | ||
| Line 59: | Line 88: | ||
<u>van Rijn formula</u> | <u>van Rijn formula</u> | ||
The reference concentration c<sub>a</sub> in the van Rijn formula is given by: | |||
{{Equation|<math>c_a = 0.015 \frac{d_{50}}{a} | {{Equation|<math>c_a = 0.015 \frac{d_{50}}{a} | ||
\left(\frac{\tau_{s,max} - \tau_{cr}}{\tau_{cr}}\right)^{1.5} d_* ^{-0.3}</math>| | \left(\frac{\tau_{s,max} - \tau_{cr}}{\tau_{cr}}\right)^{1.5} d_* ^{-0.3}</math>|12}} | ||
where a = reference height and <math>\tau_{s,max}</math> = maximum bed shear stress given by | |||
{{Equation|<math> | |||
\tau_{b,max} = \sqrt{(\tau_m + tau_w cos(\phi))^2 + (\tau_w sin(\phi))^2} | |||
</math>|13}} | |||
<table border=1 cellspacing="2"> | <table border=1 cellspacing="2"> | ||
| Line 87: | Line 124: | ||
The current-related shear stress is calculated from: | The current-related shear stress is calculated from: | ||
{{Equation|<math>\tau_c = \frac {\rho_w \kappa^2}{\left[1 + ln(k^' _s /30d) \right]^2} U_c ^2</math>| | {{Equation|<math>\tau_c = \frac {\rho_w \kappa^2}{\left[1 + ln(k^' _s /30d) \right]^2} \ U_c ^2</math>|14}} | ||
The wave-related shear stress is given as: | The wave-related shear stress is given as: | ||
{{Equation|<math>\tau_w = \rho_w \frac{f_w}{2} U_w ^2</math>| | {{Equation|<math>\tau_w = \rho_w \frac{f_w}{2} \ U_w ^2</math>|15}} | ||
{{Equation|<math>f_w = exp\lfloor 5.5(A_w /k^' _s)^{-0.2} - 6.3 \rfloor</math>| | {{Equation|<math>f_w = exp\lfloor 5.5(A_w /k^' _s)^{-0.2} - 6.3 \rfloor</math>|16}} | ||
where k<sub>s</sub><sup>'</sup> = roughness height defined as: | where k<sub>s</sub><sup>'</sup> = roughness height defined as: | ||
{{Equation|<math>k_s ^' = k_{sd} + k_{ss}</math>| | {{Equation|<math>k_s ^' = k_{sd} + k_{ss}</math>|17}} | ||
in which k<sub>sd</sub> and k<sub>ss</sub> are calculated from | in which k<sub>sd</sub> and k<sub>ss</sub> are calculated from | ||
{{Equation|<math>k_{sd} = 2.5d_{50}</math>|18}} | |||
and | |||
{{Equation|<math>k_{ss} = 5d_{50}\theta_i</math>|19}} | |||
respectively. | |||
Bed concentration in the van Rijn model is defined at the height <i>a</i> as: | Bed concentration in the van Rijn model is defined at the height <i>a</i> as: | ||
{{Equation|<math> a = max(0.5H_r , 0.01d)</math>| | {{Equation|<math> a = max(0.5H_r , 0.01d)</math>|20}} | ||
where H<sub>r</sub> = ripple height. If ripples are present, the total roughness height is modified as: | where H<sub>r</sub> = ripple height. If ripples are present, the total roughness height is modified as: | ||
{{Equation|<math>k_s = k_s ^' + k_{sf}</math>| | {{Equation|<math>k_s = k_s ^' + k_{sf}</math>|21}} | ||
where, <math>k_{sf} = 20(H_r ^2/L_r )</math> is specified for the van Rijn formula, and <math>k_{sf} = 7.5(H_r ^2/L_r) </math> is specified for the Lund-CIRP formula. The ripple dimension is obtained by selecting the largest ripple height for the case of current or waves | |||
::::::::<math> L_r = 1000d_{50}</math> | |||
{{Equation|<math>H_r = \frac{L-r}{7}</math>|22}} | |||
::<math>H_r = 0.22A_w</math> | |||
::<math>L_r = 1.25A_w \quad\quad\quad\quad \psi_w < 10</math> | |||
<math>H_r = 2.8 \ x\ 10^{-13}(250-\psi_w)^5 A_w</math> | |||
<br> | |||
{{Equation|<math>L_r = 1.4 \ x\ 10^{-6}(250-\phi_w)^2.5 A_w \quad\quad 10 \leq \psi_w < 250 </math>|23}} | |||
<br> | |||
::<math>H_r = 0</math> | |||
::<math>L_r = 0 \quad\quad\quad \psi_w > 250</math> | |||
The conversion parameter <math>\beta_d</math> to determine <math>c_0</math> is obtained from the vertical mixing coefficient. Van Rijn (1985) proposed a distribution of the mixing coefficients for only current or waves according to Figure 1. The current-related mixing coefficient is given by: | The conversion parameter <math>\beta_d</math> to determine <math>c_0</math> is obtained from the vertical mixing coefficient. Van Rijn (1985) proposed a distribution of the mixing coefficients for only current or waves according to Figure 1. The current-related mixing coefficient is given by: | ||
{{Equation|<math> \epsilon_c = \epsilon_{c,max} - \left( 1 - \frac{2z}{h} \right)^\vartheta \text{where}\ z < 0.5h | {{Equation|<math> \epsilon_c = \epsilon_{c,max} - \left( 1 - \frac{2z}{h} \right)^\vartheta \text{where}\ z < 0.5h | ||
</math>| | </math>|24}} | ||
{{Equation|<math>\epsilon_c = \epsilon_{c,max} = 0.25 \kappa u_{*c}h \ \text{where}\ z > 0.5h</math>| | {{Equation|<math>\epsilon_c = \epsilon_{c,max} = 0.25 \kappa u_{*c}h \ \text{where}\ z > 0.5h</math>|25}} | ||
where u<sub>*c</sub> = current-related bed shear velocity expressed as: | where u<sub>*c</sub> = current-related bed shear velocity expressed as: | ||
{{Equation|<math>u_{*c} = \frac{\kappa}{\left[-1 + ln\left(\frac{30d}{k_s} \right) \right]}U_c</math>| | {{Equation|<math>u_{*c} = \frac{\kappa}{\left[-1 + ln\left(\frac{30d}{k_s} \right) \right]}\ U_c</math>|26}} | ||
and <math>\vartheta</math> is a coefficient obtained from: | and <math>\vartheta</math> is a coefficient obtained from: | ||
{{Equation|<math>\vartheta = -0.25 \frac{U_w}{|U|} +2 \text{ where } 0\leq \frac{U_w}{|U|} \leq 4</math>| | {{Equation|<math>\vartheta = -0.25 \frac{U_w}{|U|} +2 \quad \text{ where } \quad 0\leq \frac{U_w}{|U|} \leq 4</math>|27}} | ||
{{Equation|<math>\vartheta = 1 \text{ where } \frac{U_w}{|U|} > 4</math>| | {{Equation|<math>\vartheta = 1 \quad \text{ where } \quad \frac{U_w}{|U|} > 4</math>|28}} | ||
[[File:tr069_fig_3.jpg|600px]] | [[File:tr069_fig_3.jpg|600px]] | ||
| Line 136: | Line 200: | ||
::<math>\ \epsilon_w = \epsilon_{w,bed} \ \ \ \ z\leq \delta</math> | ::<math>\ \epsilon_w = \epsilon_{w,bed} \ \ \ \ z\leq \delta</math> | ||
{{Equation|<math>\epsilon_w = \epsilon_{w,bed} + (\epsilon_{w,max} - \epsilon_{w,bed})\left(\frac{z - \delta}{0.5h - \delta}\right) \text { where } \delta < z \leq 0.5h </math>| | {{Equation|<math>\epsilon_w = \epsilon_{w,bed} + (\epsilon_{w,max} - \epsilon_{w,bed})\left(\frac{z - \delta}{0.5h - \delta}\right) \text { where } \delta < z \leq 0.5h </math>|29}} | ||
::<math>\ \epsilon_w = \epsilon_{w,max} \ \ \ \text{ where } z > 0.5h</math> | ::<math>\ \epsilon_w = \epsilon_{w,max} \ \ \ \text{ where } z > 0.5h</math> | ||
| Line 144: | Line 208: | ||
::<math>\epsilon_{w,bed} = 0.00065D_* \alpha_{br}\delta u_w</math> | ::<math>\epsilon_{w,bed} = 0.00065D_* \alpha_{br}\delta u_w</math> | ||
{{Equation|<math>\epsilon_{w,max} = 0.035\alpha_{br}\frac{hH}{T}</math>| | {{Equation|<math>\epsilon_{w,max} = 0.035\alpha_{br}\frac{hH}{T}</math>|30}} | ||
::<math>\alpha_{br} = 5 \left(\frac{H}{h}\right) -2 \ \ \ \text { where } H/h \geq 0.6</math> | ::<math>\alpha_{br} = 5 \left(\frac{H}{h}\right) -2 \ \ \ \text { where } H/h \geq 0.6</math> | ||
{{Equation|<math>\alpha_{br} = 1 \ \ \ \ \text{ where } H/h < 0.6</math>| | {{Equation|<math>\alpha_{br} = 1 \ \ \ \ \text{ where } H/h < 0.6</math>|31}} | ||
in which the parameter <math>\delta</math> = height from the bed given by <math>\delta = 3 H_r , H = </math> significant wave height, and T = significant wave period. If waves and current coexist, the combined mixing coefficient is given by: | in which the parameter <math>\delta</math> = height from the bed given by <math>\delta = 3 H_r , H = </math> significant wave height, and T = significant wave period. If waves and current coexist, the combined mixing coefficient is given by: | ||
{{Equation|<math>\epsilon_{cw} = \sqrt{\epsilon_c ^2 + \epsilon_w ^2} | {{Equation|<math>\epsilon_{cw} = \sqrt{\epsilon_c ^2 + \epsilon_w ^2}</math>|32}} | ||
</math>| | |||
By applying the expression for <math>\epsilon_{cw}</math>, the concentration profile can be derived from Equation 5, and the conversion parameter <math>\beta_d</math> calculated. In the AD-model based on the van Rijn equations, two methods are implemented to calculate <math>\beta_d</math>. One is based on an exponential profile employing a depth-averaged mixing coefficient <math>\overline{\epsilon}_{cw}</math>, and the other uses the original van Rijn profile, where the <math>\beta_d</math> is obtained by numerical integration of Equation 5. Assuming an exponential profile of suspended sediment concentration, <math>\beta_d</math> is obtained analytically as: | By applying the expression for <math>\epsilon_{cw}</math>, the concentration profile can be derived from Equation 5, and the conversion parameter <math>\beta_d</math> calculated. In the AD-model based on the van Rijn equations, two methods are implemented to calculate <math>\beta_d</math>. One is based on an exponential profile employing a depth-averaged mixing coefficient <math>\overline{\epsilon}_{cw}</math>, and the other uses the original van Rijn profile, where the <math>\beta_d</math> is obtained by numerical integration of Equation 5. Assuming an exponential profile of suspended sediment concentration, <math>\beta_d</math> is obtained analytically as: | ||
{{Equation|<math>\beta_d = \frac{1}{d-a} \frac{\overline{\epsilon}_{cw}}{w_f}\left[1 - exp\left(-\frac{w_f}{\overline{\epsilon}_{cw}} (d-a) \right) \right]</math>| | {{Equation|<math>\beta_d = \frac{1}{d-a} \frac{\overline{\epsilon}_{cw}}{w_f}\left[1 - exp\left(-\frac{w_f}{\overline{\epsilon}_{cw}} (d-a) \right) \right]</math>|33}} | ||
where | where | ||
{{Equation|<math>\overline{\epsilon}_{cw} = \frac{1}{d-a} \int_a ^d \epsilon_{cw}dz | {{Equation|<math>\overline{\epsilon}_{cw} = \frac{1}{d-a} \int_a ^d \epsilon_{cw}dz</math>|34}} | ||
</math>| | |||
<u>Lund-CIRP formula</u> | <u>Lund-CIRP formula</u> | ||
Latest revision as of 19:14, 9 August 2023
Equilibrium Bed load plus Advection-Diffusion Suspened load Transport model
Transport Equation
The transport equation for the suspended load is given by
|
|
(1) |
Bed Change Equation
If the advection-diffusion (A-D) equation is selected to simulate the sediment transport and mixing, the change in the water depth is calculated by the sediment continuity equation
|
|
(2) |
where is the sediment porosity, and is a bedslope coefficient.
Pick-up and Deposition Rate
The AD model calculates the bed level change due to suspended load from the difference between pick-up rate and deposition rate in
| (3) |
where qbx = bed load transport rate parallel to the x-axis, qby = bed load transport rate parallel to the y-axis, and p = porosity of sediment.
The pick-up rate and the deposition rate are also applied as the bottom boundary condition in
| (4) |
in which
- C = depth-averaged sediment concentration
- d = total depth (= h+η)
- h = still-water depth
- η = deviation of the water-surface elevation from the still-water level
- t = time
- qx = flow per unit width parallel to the x-axis (= ud)
- qy = flow per unit width parallel to the y-axis (= vd)
- u = depth-averaged current velocity parallel to the x-axis
- v = depth-averaged current velocity parallel to the y-axis
- Kx = sediment diffusion coefficient for the x direction
- Ky = sediment diffusion coefficient for the y direction
- P = sediment pick-up rate (upward sediment flux)
- D = sediment deposition rate (downward sediment flux)
The boundary conditions are specified at an arbitrary level above the mean bed level:
| (5) |
| (6) |
where c = equilibrium concentration of suspended sediment at a given elevation, and z = vertical coordinate. Both ca and c0 are reference concentrations defined at z = a. Because the upward flux of sediment depends on the bed shear stress, ca is determined from the bed shear stress calculated from the local hydrodynamic conditions. Representation of ca within CMS-M2D is dependent on selection of either the van Rijn or Lund-CIRP models. The downward sediment flux depends on the concentration in the upper water column; therefore, c0 is specified from solution of Equation 4.
Assuming that the suspended concentration is in equilibrium , then the basic equation for suspended sediment concentration can be written:
| (7) |
This equation can be solved analytically by applying an appropriate mixing coefficient , and the vertical profile of suspended concentration is obtained in the following form:
| (8) |
where F(z) is a function of the vertical concentration distribution. The relationship between the reference concentration c0 and the depth-averaged concentration C is:
| (9) |
Thus, c0 may be written in the following form by introducing a conversion function :
| (10) |
The bed level change due to suspended load is based upon the difference of
the two types of reference concentration:
| (11) |
This equation implies that erosion occurs if ca > c0, and accretion occurs if ca < c0.
In the AD model, three methods of specifying ca and c0 (that is, ) are implemented. Two of the methods are based on the van Rijn formula (van Rijn 1985) and one on the Lund-CIRP formula (Camenen and Larson 2006). Table 1 summarizes general features of the methods.
van Rijn formula
The reference concentration ca in the van Rijn formula is given by:
| (12) |
where a = reference height and = maximum bed shear stress given by
| (13) |
| Table 1 Features of Calculation of Pick-up and Deposition Rates |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| Method | Reference Concentration | Conversion Parameter | Comments |
| Exponential Profile | Eq. 10 | Eq. 24 and 25 | Fast computation. Tends to overestimate sediment transport rate. Can be used for some tests. |
| Van Rijn Profile | Eq. 10 | Solves Eq. 5 numerically with Eq. 23 (Runge-Kutta 4th) | Requires substantial computing time. Provides the same results as van Rijn (1985). |
| Lund-CIRP Profile | Eq. 70 | Eq. 24 and 72 | Fast computation. Newly developed sediment transport formula. |
The current-related shear stress is calculated from:
| (14) |
The wave-related shear stress is given as:
| (15) |
| (16) |
where ks' = roughness height defined as:
| (17) |
in which ksd and kss are calculated from
| (18) |
and
| (19) |
respectively.
Bed concentration in the van Rijn model is defined at the height a as:
| (20) |
where Hr = ripple height. If ripples are present, the total roughness height is modified as:
| (21) |
where, is specified for the van Rijn formula, and is specified for the Lund-CIRP formula. The ripple dimension is obtained by selecting the largest ripple height for the case of current or waves
| (22) |
| (23) |
The conversion parameter to determine is obtained from the vertical mixing coefficient. Van Rijn (1985) proposed a distribution of the mixing coefficients for only current or waves according to Figure 1. The current-related mixing coefficient is given by:
| (24) |
| (25) |
where u*c = current-related bed shear velocity expressed as:
| (26) |
and is a coefficient obtained from:
| (27) |
| (28) |
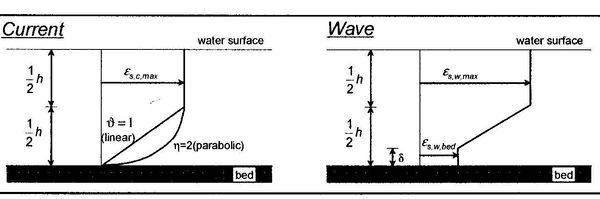 Figure 1. Vertical distributions of mixing coefficient due to current and waves
Figure 1. Vertical distributions of mixing coefficient due to current and waves
The wave-related mixing coefficient is:
| (29) |
where
| (30) |
| (31) |
in which the parameter = height from the bed given by significant wave height, and T = significant wave period. If waves and current coexist, the combined mixing coefficient is given by:
| (32) |
By applying the expression for , the concentration profile can be derived from Equation 5, and the conversion parameter calculated. In the AD-model based on the van Rijn equations, two methods are implemented to calculate . One is based on an exponential profile employing a depth-averaged mixing coefficient , and the other uses the original van Rijn profile, where the is obtained by numerical integration of Equation 5. Assuming an exponential profile of suspended sediment concentration, is obtained analytically as:
| (33) |
where
| (34) |
Lund-CIRP formula
Reference concentration and sediment diffusivity calculated by the Lund- CIRP formula may also be applied in the AD-model. The formulas used for are presented in the section describing the Lund-CIRP formula.
Boundary Conditions
There are three types of boundary conditions in the sediment transport: Wet-dry, Outflow and Inflow.
1. Wet-dry interface.
- The interface between wet and dry cells has a zero-flux boundary condition. Both the advective and diffusive fluxes are set to zero at the wet-dry interfaces. Note that avalanching may still occur between wet-dry cells.
2. Outflow Boundary Condition
- Outflow boundaries are assigned a zero-gradient boundary condition and sediments are allowed to be transported freely out of the domain.
3. Inflow Boundary Condition
- When flow is entering the domain, it is necessary to specify the sediment concentration. In CMS-Flow, the inflow sediment concentration is set to the equilibrium sediment concentation. For some cases, it is desired to reduce the amount of sediment entering from the boundary such as in locations where the sediment source is limited (i.e. coral reefs). The inflow equilibrium sediment concentration may be adjusted by multiplying by a loading scaling factor and is specified by the Advanced Card:
NET_LOADING_FACTOR <white space> #
- where # is the loading factor in dimensionless units.
References
Buttolph, A. M., C. W. Reed, N. C. Kraus, N. Ono, M. Larson, B. Camenen, H. Hanson, T. Wamsley, and A. K. Zundel. (2006). “Two-dimensional depth-averaged circulation model CMS-M2D: Version 3.0, Report 2: Sediment transport and morphology change.” Coastal and Hydraulics Laboratory Technical Report ERDC/CHL TR-06-9. Vicksburg, MS: U.S. Army Engineer Research and Development Center, U.S.A.
Camenen, B., and Larson, M. (2007). “A unified sediment transport formulation for coastal inlet application”. Technical Report ERDC-CHL CR-07-01. Vicksburg, MS: U.S. Army Engineer Research and Development Center, U.S.A
Soulsby, R. L. (1997). "Dynamics of marine sands, a manual for practical applications". H. R. Wallingford, UK: Thomas Telford.
Watanabe, A. (1987). “3-dimensional numerical model of beach evolution”. Proc. Coastal Sediments ’87, ASCE, 802-817.
Wu, W. (2004).“Depth-averaged 2-D numerical modeling of unsteady flow and nonuniform sediment transport in open channels”. J. Hydraulic Eng., ASCE, 135(10), 1013–1024.
van Rijn, L. C. (1985). “Flume experiments of sedimentation in channels by currents and waves.” Report S 347-II, Delft Hydraulics laboratory, Deflt, Netherlands.
Zhu, J. (1991). “A low diffusive and oscillation-free convection scheme”. Com. App. Num. Meth., 7, 225-232.
Zundel, A. K. (2000). “Surface-water modeling system reference manual”. Brigham Young University, Environmental Modeling Research Laboratory, Provo, UT.
External Links
- Aug 2006 Two-Dimensional Depth-Averaged Circulation Model CMS-M2D: Version 3.0, Report 2, Sediment Transport and Morphology Change [1]
- Aug 2008 CMS-Wave: A Nearshore Spectral Wave Processes Model for Coastal Inlets and Navigation Projects [2]