Flow over a bump: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(→Setup) |
(→Setup) |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
== Setup == | == Setup == | ||
The spatial domain consists of a rectangular | The spatial domain consists of a rectangular | ||
{{Equation| <math> z_b = \begin{cases} | {{Equation| <math> z_b = | ||
0 | \begin{cases} 0, & \mbox{if } x < 8 m } \\ | ||
0.2-0.05(x-10)^2 \ | 0.2-0.05(x-10)^2, & \mbox{if } 8 \leq x \leq 12 \\ | ||
0 | 0, & \mbox{if } x>12 | ||
\end{cases} | \end{cases} | ||
</math> |2=1}} | </math> |2=1}} | ||
Revision as of 23:11, 14 December 2010
UNDER CONSTRUCTION
Setup
The spatial domain consists of a rectangular
| Failed to parse (unknown function "\begin{cases}"): {\displaystyle z_b = \begin{cases} 0, & \mbox{if } x < 8 m } \\ 0.2-0.05(x-10)^2, & \mbox{if } 8 \leq x \leq 12 \\ 0, & \mbox{if } x>12 \end{cases} } | (1) |
where is the water surface elevation, is the water density, is the air density, is the gravitational acceleration, is the wind speed, is the water depth, and is a constant of integration.
Model Setup
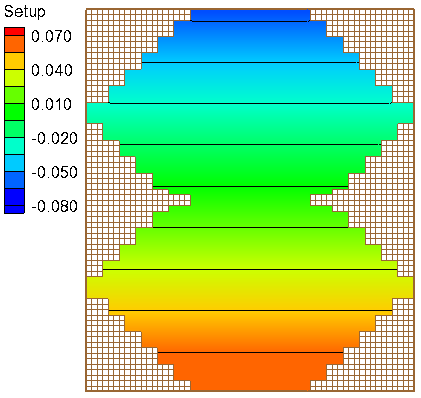
A computational grid with constant water depth of 5 m and irregular boundaries is used in order to test the model performance. The computational grid has 60 columns and 70 rows and a constant resolution of 500 m.
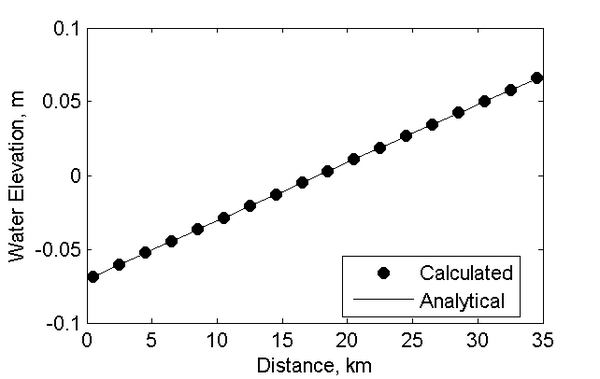
Results