Sudden Expansion: Difference between revisions
Created page with "<big> __NOTOC__ <font color=red>'''UNDER CONSTRUCTION'''</font> == Setup == The spatial domain consists of a rectangular {{Equation| <math> z_b = \begin{cases} 0, & \mb..." |
|||
| (10 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
<font color=red>'''UNDER CONSTRUCTION'''</font> | <font color=red>'''UNDER CONSTRUCTION'''</font> | ||
== Setup == | == Experimental Setup == | ||
The | The flume experiment consisted of a rectangular flume 18 m long with an inflow section 0.6 m wide which expands suddenly into a wider section 1.2 m wide. The experiment parameters are shown in Table 1. | ||
0.2 | |||
Table 1. General Settings for Sudden Expansion Case | |||
Table 1. General Settings for | |||
{|border="1" | {|border="1" | ||
|'''Parameter''' | |'''Parameter''' | ||
| Line 19: | Line 11: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Discharge | |Discharge | ||
| 0. | | 0.0385 m^3/s | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Downstream water level | |Downstream water level | ||
| 0. | | 0.0 m | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | |Manning's coefficient | ||
| | | 0.015 | ||
|} | |} | ||
== Model Setup == | == Model Setup == | ||
[[Image: | [[Image:Sudden_Expansion_Grid_V2.png|thumb|right|600px| Figure 1. Computational grid.]] | ||
The | The streched 3-level quadtree CMS-Flow grid is shown in Figure 1. The grid has a resolution between 0.03 and 0.45 m. A flux boundary condition is specified at the inflow boundary and a constant water level boundary condition is applied to the downstream boundary. The model setup parameters are shown in Table 2. | ||
Table 2. Model | |||
{|border="1" | |||
|'''Parameter''' | |||
|'''Value''' | |||
|- | |||
|Numerical scheme | |||
|Implicit | |||
|- | |||
|Time step | |||
| 30 s | |||
|- | |||
|Simulation Duration | |||
| 1 hr | |||
|- | |||
|Ramp time | |||
| 0.5 hr | |||
|} | |||
<br style="clear:both" /> | <br style="clear:both" /> | ||
| Line 36: | Line 46: | ||
== Results == | == Results == | ||
[[Image:Sudden_Expansion_Results.png|thumb|right|600px| Figure 2. Comparison of analytical and calculated water surface elevations and bed elevations.]] | [[Image:Sudden_Expansion_Results.png|thumb|right|600px| Figure 2. Comparison of analytical and calculated water surface elevations and bed elevations.]] | ||
A comparison between the analytical solution for water levels is compared to the calculated water levels in Figure 2. As shown in the goodness of fit statistics, the model results agree well with the analytical solution. The minimum water level is captured well, however there is a small shift in the location of the water level drop over the bump toward the downstream direction. | A comparison between the analytical solution for water levels is compared to the calculated water levels in Figure 2. As shown in the goodness of fit statistics in Table 3, the model results agree well with the analytical solution. The minimum water level is captured well, however there is a small shift in the location of the water level drop over the bump toward the downstream direction. | ||
Table | Table 3. Goodness of fit statistics for the current velocities | ||
{|border="1" | {|border="1" | ||
|'''Statistic''' | |'''Statistic''' ||'''x = 0 m''' || '''x = 1 m''' || '''x = 2 m''' || '''x = 3 m''' || '''x = 4 m''' || '''x = 5 m''' | ||
|''' | |||
|- | |- | ||
|RMSE | |RMSE, m/s || 0.0105 || 0.0260 || 0.0294 || 0.0386 || 0.0775 || 0.0584 | ||
| 0. | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | |NMAE, % || 1.28 || 0.72 || 0.56 || 3.19 || 4.33 || 0.45 | ||
| 0. | |||
|- | |- | ||
|R^2 | |R^2 || 0.789 || 0.995 || 0.990 || 0.989 || 0.936 || 0.980 | ||
| 0. | |||
|- | |- | ||
|Bias | |Bias, m/s || -0.0083 || -0.0046 || 0.0035 || 0.0187 || -0.0017 || 0.0022 | ||
| 0.0017 | |||
|} | |} | ||
* For a definition of the goodness of fit statistics see [[Statistics | Goodness of fit statistics]]. | |||
<br style="clear:both" /> | <br style="clear:both" /> | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
* | *Xie, B.L. (1996). "Experiment on flow in a sudden-expanded channel," Technical Report, Wuhan University of Hydraulic and Electric Engineering, China. | ||
---- | ---- | ||
Latest revision as of 17:35, 1 June 2011
UNDER CONSTRUCTION
Experimental Setup
The flume experiment consisted of a rectangular flume 18 m long with an inflow section 0.6 m wide which expands suddenly into a wider section 1.2 m wide. The experiment parameters are shown in Table 1.
Table 1. General Settings for Sudden Expansion Case
| Parameter | Value |
| Discharge | 0.0385 m^3/s |
| Downstream water level | 0.0 m |
| Manning's coefficient | 0.015 |
Model Setup
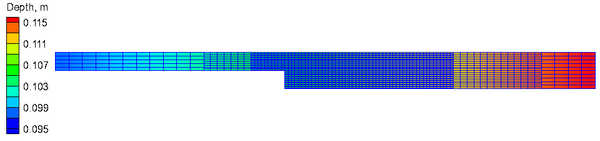
The streched 3-level quadtree CMS-Flow grid is shown in Figure 1. The grid has a resolution between 0.03 and 0.45 m. A flux boundary condition is specified at the inflow boundary and a constant water level boundary condition is applied to the downstream boundary. The model setup parameters are shown in Table 2.
Table 2. Model
| Parameter | Value |
| Numerical scheme | Implicit |
| Time step | 30 s |
| Simulation Duration | 1 hr |
| Ramp time | 0.5 hr |
Results
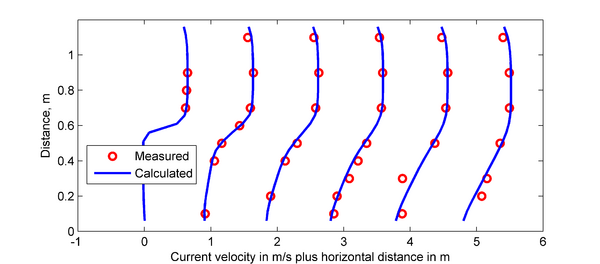
A comparison between the analytical solution for water levels is compared to the calculated water levels in Figure 2. As shown in the goodness of fit statistics in Table 3, the model results agree well with the analytical solution. The minimum water level is captured well, however there is a small shift in the location of the water level drop over the bump toward the downstream direction.
Table 3. Goodness of fit statistics for the current velocities
| Statistic | x = 0 m | x = 1 m | x = 2 m | x = 3 m | x = 4 m | x = 5 m |
| RMSE, m/s | 0.0105 | 0.0260 | 0.0294 | 0.0386 | 0.0775 | 0.0584 |
| NMAE, % | 1.28 | 0.72 | 0.56 | 3.19 | 4.33 | 0.45 |
| R^2 | 0.789 | 0.995 | 0.990 | 0.989 | 0.936 | 0.980 |
| Bias, m/s | -0.0083 | -0.0046 | 0.0035 | 0.0187 | -0.0017 | 0.0022 |
- For a definition of the goodness of fit statistics see Goodness of fit statistics.
References
- Xie, B.L. (1996). "Experiment on flow in a sudden-expanded channel," Technical Report, Wuhan University of Hydraulic and Electric Engineering, China.