CMS-Flow:Model Control:Sediment Transport: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
mNo edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
*Maximum bed layer thickness | *Maximum bed layer thickness | ||
*Bed layer block (choose number of layers and various datasets). | *Bed layer block (choose number of layers and various datasets). | ||
{{Image| | {{Image|CMS_ModelControl_SedimentTransport2.png|500px|Link=|}} | ||
==Scaling factors and coefficients== | ==Scaling factors and coefficients== | ||
*Bed load scaling factor | *Bed load scaling factor | ||
Latest revision as of 21:51, 22 July 2024
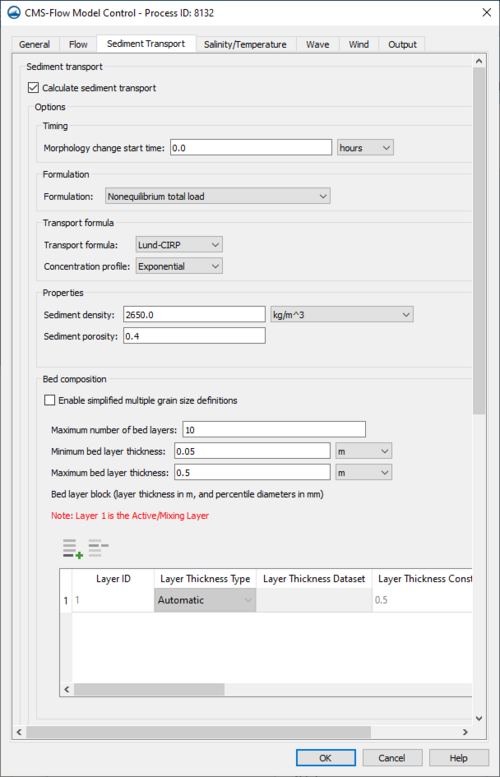
Timing
- Morphology change start time
Formulation
- Formulation selection
Transport Formula
- Transport formula
- Concentration profile
Properties
- Sediment density
- Sediment porosity
Bed Composition
Either Simplified or Normal selection can be chosen.
Simplified
- Multiple grain size selection
- Number of size classes
- Bed composition input selection
- Sediment standard deviation
- D50 bed layer definition
- Number of bed layers
- Constant thickness for mixing layer
- Constant thickness for bed layers
Normal
- Maximum number of bed layers
- Minimum bed layer thickness
- Maximum bed layer thickness
- Bed layer block (choose number of layers and various datasets).
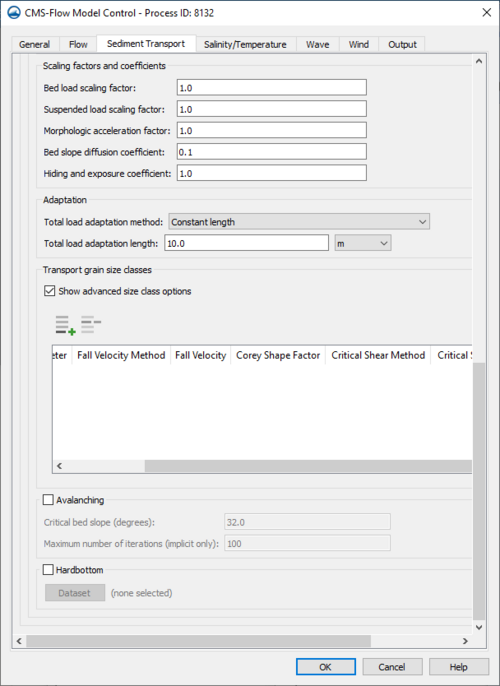
Scaling factors and coefficients
- Bed load scaling factor
- Suspended load scaling factor
- Morphologic acceleration factor
- Bed slope diffusion coefficient
- Hiding and exposure coefficient
Adaptation
- Total load adaptation method selection
- Total load adaptation length
Transport grain size classes
- Choose number of grain sizes
- Diameter
- Fall velocity method
- Fall velocity
- Corey Shape factor
- Critical shear method
- Critical shear stress
Avalanching
- Critical Bed slope
- Maximum number of iterations
Hard Bottom
- Hard bottom dataset selection