CMS-Flow Boundary Conditions: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
|||
| (31 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__TOC__ | |||
[[Image:CMS-Flow_Boundary_Conditions_Window.PNG|thumb|right| | [[Image:CMS-Flow_Boundary_Conditions_Window.PNG|thumb|right|400px| Figure 1. CMS-Flow Boundary Conditions window]] | ||
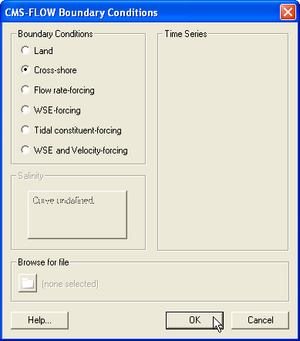
CMS-Flow has five types of boundary conditions which are listed and discussed below. The figure below shows the CMS-Flow Boundary Conditions window in SMS. All CMS-Flow boundary conditions are forced at the edges of the domain by use of cellstrings defined with the Surfacewater Modeling System (SMS). Cellstrings can either be created manually or using the SMS tool called ''Generate Along Boundary'' which is found under the ''Cellstring'' menu. | CMS-Flow has five types of boundary conditions which are listed and discussed below. The figure below shows the CMS-Flow Boundary Conditions window in SMS. All CMS-Flow boundary conditions are forced at the edges of the domain by use of cellstrings defined with the Surfacewater Modeling System (SMS). Cellstrings can either be created manually or using the SMS tool called ''Generate Along Boundary'' which is found under the ''Cellstring'' menu. | ||
<br style="clear:both" /> | <br style="clear:both" /> | ||
= | =Creating Cell Strings= | ||
[[Image:Generate_Cellstring.png|thumb|right|400px|Figure 2. Automated cellstring generation in SMS 11.0]] | |||
Cell strings can either be manually created by clicking on the cells or by using the SMS interface to automatically detect and assign the cell strings. | |||
==Flow Rate-Forcing | * To manually create a cellstring | ||
# Select the ''Create cellstring'' tool. | |||
# Single-click on the first cell of the cellstring. | |||
# If necessary, single click on subsequent cells in the cellstring (around corners). | |||
# Double-click on the last cellstring to finish. | |||
* To automatically generate cellstring in SMS | |||
# Click on ''Cellstring'' | ''Generate Cellstrings'' and select one of the options: | |||
## ''Along Open Boundaries'' | |||
## ''Along Land Boundaries'' | |||
## ''Along Open and Land Boundaries'' | |||
* '''Notes:''' | |||
# Cell strings must be at least three cells wide. | |||
# Cell strings must cover ALL open boundaries. Leaving any open boundaries without an assigned boundary will close that boundary and apply a wall boundary condition. | |||
# Land boundary conditions are not necessary at close boundaries (cells next to inactive cells). The CMS will automatically detect these land boundaries. | |||
# The orientation of cellstrings is important. Some inflow and all outflow boundary conditions assume a zero-gradient in the normal direction. If this assumption is not valid, the boundary may produce instability problems. It is recommended that the boundaries be placed in a orientation such that the spatial gradients normal to the cellstring or minimal. | |||
=Land Boundary= | |||
The land boundary conditions is equivalent to a zero flux boundary condition. The land boundary condition is the default boundary condition when a cell string is created. It is not necessary to define land boundaries in the interior of the CMS-Flor domain, since land boundarys will automatically be detected by CMS-Flow based on the local water depths and the presence of inactive land cells. | |||
=Flow Rate-Forcing= | |||
The flow rate boundary condition specifies a time series of water fluxes in units of m^3/s per cell. | The flow rate boundary condition specifies a time series of water fluxes in units of m^3/s per cell. | ||
| Line 13: | Line 35: | ||
* Total flow rate specified is divided between the total number of cells in the cellstring with each carrying a portion of the total. | * Total flow rate specified is divided between the total number of cells in the cellstring with each carrying a portion of the total. | ||
* This boundary type may only be specified along cell strings which are straight. | * This boundary type may only be specified along cell strings which are straight. | ||
* | * Positive values are always directed INTO the domain and negative values are LEAVING the domain. | ||
** Note: Previous versions of CMS (v4.0 and earlier) treated flow boundaries differently. | |||
== | ==Previous Flow Rate Guidelines== | ||
* The sign of the flow rate curve was dependent on the direction of flow with respect to the origin (always lower-left hand corner of the grid). | |||
:This guide should assist in proper assignment: | |||
:* Flow rate from the East - Negative value | |||
:* Flow rate from the West - Positive value | |||
:* Flow rate from the North - Negative value | |||
:* Flow rate from the South - Positive value | |||
=Water Surface Elevation Forcing= | |||
Two types of Water Surface Elevation Forcing exist for CMS-Flow. Once a water surface elevation curve (or series of curves) is applied, the user is able to display the curve information graphically. | |||
== 1. Single time series curve for each cell string (Option "Define curve" in SMS) == | |||
[[Image:Shark_Fig19.PNG|thumb|right|400px|Figure 3. Selecting the cellstring along the ocean boundary, and clicking on]] | |||
For this type of BC, a single time series of water levels is specified and is applied at all of the cells along a boundary cell string. The time series curve may be specified by either importing an SMS *.xys file, copying tabular data into SMS, or manually entered the time series information in SMS. To assign this type of BC in SMS: | |||
# Click on the ''Select a Cellstring'' button, right-click the blue cellstring along the ocean boundary (if this cannot be selected it is because all cellstrings were deleted; this can be regenerated by clicking and clicking around the ocean cells or selecting ''Cellstring'' and ''Generate Along Boundary''), select ''Assign BC'' (Figure 1). | |||
# Select the ''WSE-forcing'' boundary condition, and click curve undefined (Figure 2) | |||
# Copy-paste a time series into the ''XY Series Editor'' (Figure 2), | |||
# Click on the ''Export'' button to save the water level time series to an SMS xys file (time series file). | |||
# Save the ''SMS project File'' (*.sms) or ''CMS-Flow Simulation File'' (*.cmcards). | |||
[[Image:Shark_Fig20.PNG|thumb|none|300px|Figure 4. Top: is the blank ''''''''XY Series Editor''''''''; Bottom: after the data is pasted in.]] | |||
<br style="clear:both" /> | |||
User | == 2. Time series curve for each cell on cell string (Option "Extract from data set" in SMS) == | ||
User creates a cellstring for the given boundary and extracts multiple time series curves from a dataset or database. Each cell along the cellstring is given its own time-series curve information. Examples are: | |||
* Extraction of water surface elevation values from a larger domain solution (ie. Larger CMS-Flow or ADCIRC grid) | * Extraction of water surface elevation values from a larger domain solution (ie. Larger CMS-Flow or ADCIRC grid) | ||
* Extraction of tidal constituent information from a tidal database, from which a water surface elevation curve can be generated. | * Extraction of tidal constituent information from a tidal database, from which a water surface elevation curve can be generated. | ||
=Tidal Constituent Forcing= | |||
[[Image:CMS-Flow_Model_Control_Tidal.png|thumb|right|500px|Figure 5. Tidal Constituent Forcing window in SMS]] | |||
[[Image:CMS-Flow_Model_Control_Tidal.png|thumb|right|500px|Tidal Constituent Forcing window in SMS]] | |||
CMS-Flow as the option of forcing with a harmonic tidal water surface elevation. To assign a boundary as a tidal boundary: | CMS-Flow as the option of forcing with a harmonic tidal water surface elevation. To assign a boundary as a tidal boundary: | ||
# Select a cellstring | # Select a cellstring | ||
# Click under ''CMS-Flow | Assign | # Click under ''CMS-Flow | Assign BC | ||
# In the ''CMS-Flow Boundary Conditions'' window, click on ''Tidal constituent-forcing'', and click ''OK''. | # In the ''CMS-Flow Boundary Conditions'' window, click on ''Tidal constituent-forcing'', and click ''OK''. | ||
# Open the ''CMS-Flow Model Control'' window and click on the tab labeled ''Tidal''. | # Open the ''CMS-Flow Model Control'' window and click on the tab labeled ''Tidal''. | ||
# Enter the amplitudes and phases of the tidal constituents. Note that the same amplitude and phase are applied to entire cellstring and click ''OK'' | # Enter the amplitudes and phases of the tidal constituents. Note that the same amplitude and phase are applied to entire cellstring and click ''OK'' | ||
Tidal constituents used in CMS | '''Table 1. Tidal constituents used in CMS''' | ||
{| border="1" | {| border="1" | ||
! Constituent !! Speed !! Constituent !! Speed !! Constituent !! Speed !! Constituent !! Speed | ! Constituent !! Speed !! Constituent !! Speed !! Constituent !! Speed !! Constituent !! Speed | ||
| Line 94: | Line 105: | ||
<br style="clear:both" /> | <br style="clear:both" /> | ||
=Water Surface Elevation and Velocity Forcing= | |||
[[Image:WSEandVelocity-forcing.png|thumb|right|400px|Figure 6. Selecting the ''WSE and Velocity-forcing'' boundary condition in the ''CMS-FLOW Boundary Conditions'' window. ]] | |||
When nesting a CMS-Flow grid within a larger CMS-Flow or ADCIRC grid, it is possible to extract both water levels and velocities from the larger grid. These values are internally converted into fluxes at the boundary cell faces. | |||
* To extract water surface elevations and velocities from a larger grid:: | |||
:# Load both the nested CMS-Flow grid. | |||
:# Load the larger CMS-Flow or ADCIRC grid along with the solution file. | |||
:# Select the appropriate boundary cellstring and either go to ''CMS-FLOW'' | ''Assign BC'' or right-click on the cellstring and select ''Assign BC''. | |||
:# In the ''CMS-FLOW Boundary Conditions'' window, select ''WSE and Velocity-forcing''. | |||
:# Click on ''Extract'' under the ''Time Series'' section. | |||
:# In the ''Extract Boundary Conditions'' window, select the water surface elevation dataset under the section called ''Regional scalar model solution:'', and select the current velocity dataset (vector dataset) under the section called ''Regional vector model solution:''. | |||
:# Click on ''Extract''. The extraction process may take several minutes. Be patient and DO NOT click or press any keys in SMS as this may cause the interface to crash. | |||
[[Image:Extract_WSE_Vel.png|thumb|none|300px|Figure 7. Extracting water surface elevations and current velocities from a larger grid solution.]] | |||
<br style="clear:both" /> | |||
= Cross-shore Boundary = | |||
[[Image:Cross-shore_BC_setup.png|thumb|right|400px|Figure 8. Setting up a cross-shore boundary condition cellstring.]] | |||
For a well-defined hydrodynamic problem, the flow discharge or velocity is needed at inflow boundaries, while the water level is usually given at outflow boundaries for a subcritical flow or at inflow boundaries for a supercritical flow. For most coastal applications, the water surface elevation is usually specified at the seaward ocean boundary, which can be the time series of tide levels recorded at the boundary, generated using tidal constituents, or predicted using a larger-scale regional model. Along the cross-shore, constant water surface elevation is not appropriate since winds and waves will produce a setup in the water levels. Also, extracted water levels from a larger grid solution may be too coarse to properly describe the nearshore longshore currents and water levels. A better approach is the use one-dimensional solution to the momentum equations to predict an inflow water flux and outflow water surface elevation. | |||
* To create a cross-shore boundary condition: | |||
:# Select the appropriate cellstring and either right-click and select ''Assign BC'' or go to ''CMS-FLOW'' | ''Assign BC'' | |||
:# In the ''CMS-FLOW Boundary COnditions'' window, select ''Cross-shore'' under ''Boundary Conditions'' and click ''OK'' | |||
[[Image:Assign_CSBC.png|thumb|none|300px|Figure 9. Setting up a cross-shore boundary condition cellstring.]] | |||
= Nesting = | |||
[[CMS-Flow_Boundary_Conditions/Tidal_Database_Nesting | CMS Internal Nesting Tidal Boundary Condition with Constituent Database]] | |||
[[CMS-Flow_Boundary_Conditions/WSE_Nesting | CMS Internal Nesting WSE Boundary Condition with Parent Grid]] | |||
<br style="clear:both" /> | |||
---- | ---- | ||
[[CMS#Documentation_Portal | Documentation Portal]] | [[CMS#Documentation_Portal | Documentation Portal]] | ||
Latest revision as of 14:27, 7 April 2023
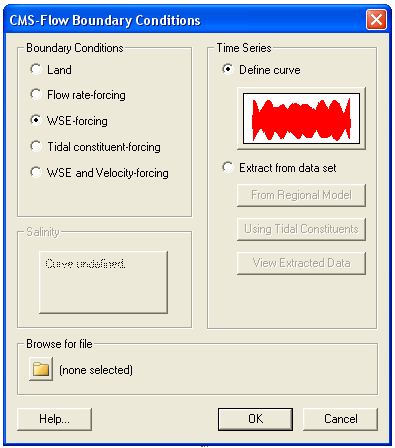
CMS-Flow has five types of boundary conditions which are listed and discussed below. The figure below shows the CMS-Flow Boundary Conditions window in SMS. All CMS-Flow boundary conditions are forced at the edges of the domain by use of cellstrings defined with the Surfacewater Modeling System (SMS). Cellstrings can either be created manually or using the SMS tool called Generate Along Boundary which is found under the Cellstring menu.
Creating Cell Strings
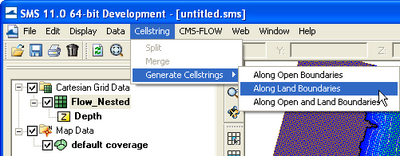
Cell strings can either be manually created by clicking on the cells or by using the SMS interface to automatically detect and assign the cell strings.
- To manually create a cellstring
- Select the Create cellstring tool.
- Single-click on the first cell of the cellstring.
- If necessary, single click on subsequent cells in the cellstring (around corners).
- Double-click on the last cellstring to finish.
- To automatically generate cellstring in SMS
- Click on Cellstring | Generate Cellstrings and select one of the options:
- Along Open Boundaries
- Along Land Boundaries
- Along Open and Land Boundaries
- Notes:
- Cell strings must be at least three cells wide.
- Cell strings must cover ALL open boundaries. Leaving any open boundaries without an assigned boundary will close that boundary and apply a wall boundary condition.
- Land boundary conditions are not necessary at close boundaries (cells next to inactive cells). The CMS will automatically detect these land boundaries.
- The orientation of cellstrings is important. Some inflow and all outflow boundary conditions assume a zero-gradient in the normal direction. If this assumption is not valid, the boundary may produce instability problems. It is recommended that the boundaries be placed in a orientation such that the spatial gradients normal to the cellstring or minimal.
Land Boundary
The land boundary conditions is equivalent to a zero flux boundary condition. The land boundary condition is the default boundary condition when a cell string is created. It is not necessary to define land boundaries in the interior of the CMS-Flor domain, since land boundarys will automatically be detected by CMS-Flow based on the local water depths and the presence of inactive land cells.
Flow Rate-Forcing
The flow rate boundary condition specifies a time series of water fluxes in units of m^3/s per cell.
NOTES:
- Total flow rate specified is divided between the total number of cells in the cellstring with each carrying a portion of the total.
- This boundary type may only be specified along cell strings which are straight.
- Positive values are always directed INTO the domain and negative values are LEAVING the domain.
- Note: Previous versions of CMS (v4.0 and earlier) treated flow boundaries differently.
Previous Flow Rate Guidelines
- The sign of the flow rate curve was dependent on the direction of flow with respect to the origin (always lower-left hand corner of the grid).
- This guide should assist in proper assignment:
- Flow rate from the East - Negative value
- Flow rate from the West - Positive value
- Flow rate from the North - Negative value
- Flow rate from the South - Positive value
Water Surface Elevation Forcing
Two types of Water Surface Elevation Forcing exist for CMS-Flow. Once a water surface elevation curve (or series of curves) is applied, the user is able to display the curve information graphically.
1. Single time series curve for each cell string (Option "Define curve" in SMS)
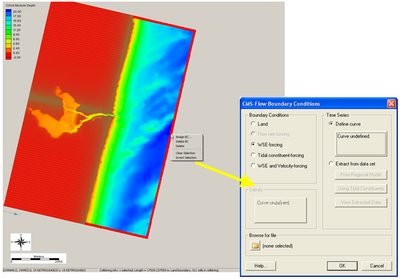
For this type of BC, a single time series of water levels is specified and is applied at all of the cells along a boundary cell string. The time series curve may be specified by either importing an SMS *.xys file, copying tabular data into SMS, or manually entered the time series information in SMS. To assign this type of BC in SMS:
- Click on the Select a Cellstring button, right-click the blue cellstring along the ocean boundary (if this cannot be selected it is because all cellstrings were deleted; this can be regenerated by clicking and clicking around the ocean cells or selecting Cellstring and Generate Along Boundary), select Assign BC (Figure 1).
- Select the WSE-forcing boundary condition, and click curve undefined (Figure 2)
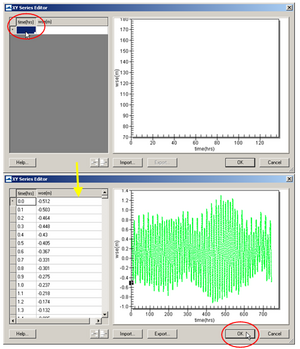
- Copy-paste a time series into the XY Series Editor (Figure 2),
- Click on the Export button to save the water level time series to an SMS xys file (time series file).
- Save the SMS project File (*.sms) or CMS-Flow Simulation File (*.cmcards).
2. Time series curve for each cell on cell string (Option "Extract from data set" in SMS)
User creates a cellstring for the given boundary and extracts multiple time series curves from a dataset or database. Each cell along the cellstring is given its own time-series curve information. Examples are:
- Extraction of water surface elevation values from a larger domain solution (ie. Larger CMS-Flow or ADCIRC grid)
- Extraction of tidal constituent information from a tidal database, from which a water surface elevation curve can be generated.
Tidal Constituent Forcing
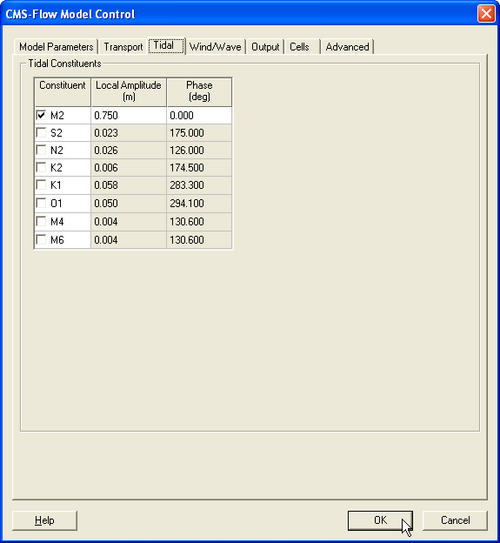
CMS-Flow as the option of forcing with a harmonic tidal water surface elevation. To assign a boundary as a tidal boundary:
- Select a cellstring
- Click under CMS-Flow | Assign BC
- In the CMS-Flow Boundary Conditions window, click on Tidal constituent-forcing, and click OK.
- Open the CMS-Flow Model Control window and click on the tab labeled Tidal.
- Enter the amplitudes and phases of the tidal constituents. Note that the same amplitude and phase are applied to entire cellstring and click OK
Table 1. Tidal constituents used in CMS
| Constituent | Speed | Constituent | Speed | Constituent | Speed | Constituent | Speed |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SA* | 0.041067 | SSA* | 0.082137 | MM* | 0.54438 | MSF* | 1.0159 |
| MF* | 1.098 | 2Q1* | 12.8543 | Q1* | 13.3987 | RHO1* | 13.4715 |
| O1* | 13.943 | M1* | 14.4967 | P1* | 14.9589 | S1* | 15.0 |
| K1* | 15.0411 | J1* | 15.5854 | OO1* | 16.1391 | 2N2* | 27.8954 |
| MU2* | 27.9682 | N2* | 28.4397 | NU2* | 28.5126 | M2 | 28.9841 |
| LDA2* | 29.4556 | L2* | 29.5285 | T2* | 29.9589 | S2 | 30 |
| R2* | 30.0411 | K2 | 30.0821 | 2SM2* | 31.0159 | 2MK3* | 42.9271 |
| M3* | 43.4762 | MK3* | 44.0252 | MN4* | 57.4238 | M4 | 57.9682 |
| MS4* | 58.9841 | S4* | 60.0 | M6 | 86.9523 | S6* | 90.0 |
| M8* | 115.9364 |
* Only available through advanced cards for CMS >v4.0
Water Surface Elevation and Velocity Forcing
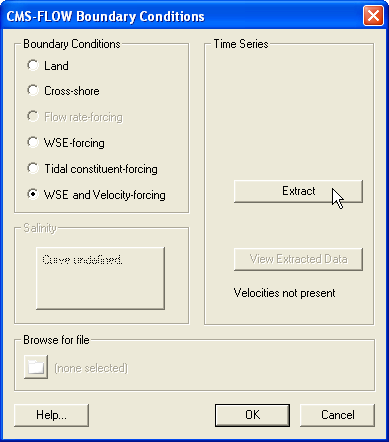
When nesting a CMS-Flow grid within a larger CMS-Flow or ADCIRC grid, it is possible to extract both water levels and velocities from the larger grid. These values are internally converted into fluxes at the boundary cell faces.
- To extract water surface elevations and velocities from a larger grid::
- Load both the nested CMS-Flow grid.
- Load the larger CMS-Flow or ADCIRC grid along with the solution file.
- Select the appropriate boundary cellstring and either go to CMS-FLOW | Assign BC or right-click on the cellstring and select Assign BC.
- In the CMS-FLOW Boundary Conditions window, select WSE and Velocity-forcing.
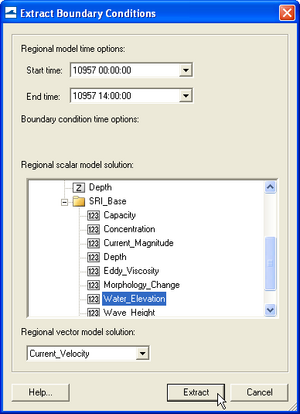
- Click on Extract under the Time Series section.
- In the Extract Boundary Conditions window, select the water surface elevation dataset under the section called Regional scalar model solution:, and select the current velocity dataset (vector dataset) under the section called Regional vector model solution:.
- Click on Extract. The extraction process may take several minutes. Be patient and DO NOT click or press any keys in SMS as this may cause the interface to crash.
Cross-shore Boundary
For a well-defined hydrodynamic problem, the flow discharge or velocity is needed at inflow boundaries, while the water level is usually given at outflow boundaries for a subcritical flow or at inflow boundaries for a supercritical flow. For most coastal applications, the water surface elevation is usually specified at the seaward ocean boundary, which can be the time series of tide levels recorded at the boundary, generated using tidal constituents, or predicted using a larger-scale regional model. Along the cross-shore, constant water surface elevation is not appropriate since winds and waves will produce a setup in the water levels. Also, extracted water levels from a larger grid solution may be too coarse to properly describe the nearshore longshore currents and water levels. A better approach is the use one-dimensional solution to the momentum equations to predict an inflow water flux and outflow water surface elevation.
- To create a cross-shore boundary condition:
- Select the appropriate cellstring and either right-click and select Assign BC or go to CMS-FLOW | Assign BC
- In the CMS-FLOW Boundary COnditions window, select Cross-shore under Boundary Conditions and click OK
Nesting
CMS Internal Nesting Tidal Boundary Condition with Constituent Database
CMS Internal Nesting WSE Boundary Condition with Parent Grid