CSMART: Difference between revisions
*>Anonymous |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (27 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
=''' Coastal Structures Management, Analysis, and Ranking Tool (CSMART) '''= | =''' Coastal Structures Management, Analysis, and Ranking Tool (CSMART) '''= | ||
[[Image:CSMART Main Page.png|500px|thumb|Right|CSMART and CSMART Silverlight Edition]] | |||
The Coastal Structures Management, Analysis, and Ranking Tool (CSMART) is an internet application being developed in the Coastal Inlets Research Program (CIRP) for prioritization of coastal jetties and breakwaters in OM budget development. CSMART may be accessed at https://cpt.usace.army.mil/Structures with CAC authentication, additionally the developmental version of CSMART Silverlight Edition may be accessed at https://itlgis01.usace.army.mil/csmart/. | |||
CSMART accesses a variety of data sets that provide indicators of coastal structure significance. For example, metrics for economic activity supported by coastal structures include commercial tonnage in associated channels, nearby commercial fish landings, and associated cruise and ferry passenger statistics. These and other selected metrics are analyzed to produce customized rankings of coastal structures according to user-specified filters and search criteria. The final rankings can be exported and saved for later viewing, or used to generate Google Earth™ overlays for visualizations. CSMART is designed for use by personnel at the District, Division, and HQ levels of Corps management. | |||
| Line 10: | Line 17: | ||
CSMART is developmental software that is updated frequently. | CSMART is developmental software that is updated frequently. | ||
<br style=clear:both /> | |||
=''' CSMART | =''' CSMART General Layout '''= | ||
CSMART is organized into a series of steps (see Figure 1) to guide the user in filtering the query, picking locations for analysis, and displaying the results. Step 1 is titled: Features. These are commercial tonnage, coast guard incidents, dredging, and other metrics which can be selected by the user. Step 2: Structures; allows the user to specify the structures to include in the analysis. The structures are organized by district. Step 3: Execute Query. Once all selections have been made the query is executed. Step 4: View Results. After completing the query CSMART ranks each of the structures selected in Step 2 according to each of the metrics chosen in Step 1 individually. A global ranking incorporating all the selected features and structures may also be executed during this step. | |||
[[Image:HomeScreen_Features.jpg|400px|thumb|left|Fig. 1 – Steps Tabs]] | |||
<br style=clear:both /> | |||
='' | =='' Step 1: Features ''== | ||
Step 1 prompts the user to select which features to include in the analysis. The features include: commercial tonnage, commercial fishing, coast guard incidents, dredging, cruise data, ferry data, boat ramps/marinas, binary choices, and structure condition ratings. These metrics are accessed via the sub-tabs as shown in Figure 2. | |||
[[Image:HomeScreen_Features2.jpg|400px|thumb|left|Fig. 2 – Features Tabs]] | |||
<br style=clear:both /> | |||
The user may select one or more of the sub-tabs for the analysis by clicking on the tab and checking the “Include?” box. Once a sub-tab has been selected the user can choose what data within each sub-tab to include in the query. For example, under the commercial tonnage sub-tab, selections for movement, year, and commodity are available. After all selections within a sub-tab are made the Save Filter Selections button must be pushed in order for the selections to be included in the analysis. The user may then move to other sub-tabs and make similar selections to filter the query. | |||
Data for commercial tonnage, coast guard incidents, and dredging were obtained from the US Army Corps of Engineers (USACE) Navigation Data Center (http://www.ndc.iwr.usace.army.mil/index.htm). Commercial fishing data were taken from The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s National Marine Fisheries Service (NOAA-NMFS). Cruise data were obtained from the US Dept of Transportation’s Maritime Administration and Ferry data from Research and Innovative Technology Administration (RITA) Bureau of Transportation Statistics (BTS). Boat Ramp locations were from multiple sources. A nationwide database from EarthNC was supplemented by other sources for many individual coastal states. Binary choices allow the user to include structures that support a harbor of refuge, a subsistence harbor, public transportation, a military base, etc. These data come from project usage codes maintained by the Navigation Business Line at USACE-HQ. Finally, structure condition ratings were obtained from communications with district personnel. Commercial tonnage and cruise data are hard-linked to Corps structures, whereas the other data sets are spatially joined to selected structures by a user specified search radius. Figure 3 shows a one mile search radius around the East Arrowhead Breakwater in Cleveland. The red pins represent Coast Guard incidents, the yellow represent boat ramps and marinas, and the green represents dredging events that took place within the search radius. | |||
[[Image:SearchRadius.jpg|400px|thumb|left|Fig. 3 – All selected data within the user specified search radius is credited to the structure for analysis]] | |||
<br style=clear:both /> | |||
=='' Step 2: | =='' Step 2: Structures ''== | ||
CSMART allows the user to | CSMART allows the user to select any of the Corps coastal structures for analyses and comparison. By clicking the Step 2: Structures Tab, a drop down tree organized into USACE districts appears. This tree is organized into a hierarchy containing districts, projects and individual structures. The user may click the small triangles to open the next level of the hierarchy. Structures may be chosen for analysis at each level in the tree by clicking the small box next to the desired selection. Once all selections have been made the user must push the Save Filter Selections button in order for the structures to be included in the analysis. | ||
[[Image: | [[Image:StructuresTab.jpg|400px|thumb|left|Fig. 4 – Structures Tab]] | ||
<br style= | <br style=clear:both /> | ||
=='' Step 3: Execute Query ''== | =='' Step 3: Execute Query ''== | ||
| Line 44: | Line 52: | ||
=='' Step 4: View Results ''== | =='' Step 4: View Results ''== | ||
The results for each of the features selected in Step 1 are available to the user by clicking on the appropriate sub-tab under the View Results Tab. By selecting one of the sub-tabs CSMART will display each of the selected structures with its associated rank and data. Figure 5 shows the tonnage results of all the structures within CSMART for 2006 (Note: CSMART does not include local or internal traffic in tonnage totals). Notice that when a sub-tab is selected that was not included by the user a message is displayed saying the feature was not included in the analysis. | |||
[[Image: | [[Image:ViewResults_Tonnage.jpg|400px|thumb|left|Fig. 5 – Tonnage output for 2006 under the View Results Tab]] | ||
<br style= | <br style=clear:both /> | ||
After looking at the results for a particular feature the user may want a more detailed look at a particular structure. In this case the user may click on the row containing the desired structure and a new sub-tab will appear with the structure name. Selecting the new sub-tab will show the user a more detailed breakdown of the particular feature for the selected structure. For example, by clicking the row corresponding to LA-LB Harbors San Pedro Breakwater, California under the tonnage sub-tab the data shown in Figure 6 is displayed. | |||
[[Image: | [[Image:Tonnage_Details.jpg|400px|thumb|left|Fig. 6 – 2006 Tonnage details for the San Pedro Breakwater]] | ||
<br style= | <br style=clear:both /> | ||
In addition to ranking structures according to each feature individually a global ranking of structures incorporating all of the selected features may also be executed. By selecting the Global Ranking sub-tab the user may set a weight for each feature. The total of all the weights entered must be equal to one. By weighting each feature the user can specify how much he/she wants each feature to be counted toward the global ranking of the structures (see Figure 7). | |||
[[Image: | [[Image:Weightings.jpg|400px|thumb|left|Fig. 7 – Weighting of each feature for global ranking of structures]] | ||
<br style= | <br style=clear:both /> | ||
Once all the weightings have been entered the user must click the Update Weightings button. Next the Global Rankings sub-tab may be selected, which will generate a table with a normalized ranking for each structure under each of the selected features. CSMART also computes an overall structure ranking and sorts the table accordingly. Figure 8 shows an example of the global rankings table. | |||
[[Image:GlobalRankingsTable.jpg|400px|thumb|left|Fig. 8 – Global Rankings Table]] | |||
<br style=clear:both /> | |||
The global rankings generated by CSMART are an initial screening of structures, not an in depth analysis of the structures that are most deserving of OM funding. The goal of CSMART is to assist OM decision makers in focusing their efforts on structures ranked by several general measures of significance. | |||
Latest revision as of 19:30, 1 November 2013
Coastal Structures Management, Analysis, and Ranking Tool (CSMART)
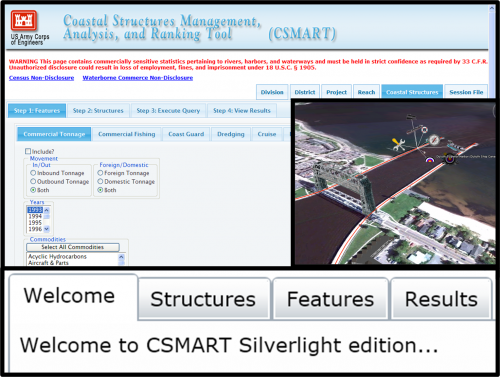
The Coastal Structures Management, Analysis, and Ranking Tool (CSMART) is an internet application being developed in the Coastal Inlets Research Program (CIRP) for prioritization of coastal jetties and breakwaters in OM budget development. CSMART may be accessed at https://cpt.usace.army.mil/Structures with CAC authentication, additionally the developmental version of CSMART Silverlight Edition may be accessed at https://itlgis01.usace.army.mil/csmart/.
CSMART accesses a variety of data sets that provide indicators of coastal structure significance. For example, metrics for economic activity supported by coastal structures include commercial tonnage in associated channels, nearby commercial fish landings, and associated cruise and ferry passenger statistics. These and other selected metrics are analyzed to produce customized rankings of coastal structures according to user-specified filters and search criteria. The final rankings can be exported and saved for later viewing, or used to generate Google Earth™ overlays for visualizations. CSMART is designed for use by personnel at the District, Division, and HQ levels of Corps management.
POC: Dr. Kenneth Ned Mitchell
<br\>Kenneth.n.mitchell@usace.army.mil
<br\>601-634-2022
<br\>US Army Engineer Research and Development Center (ERDC)
<br\>Coastal and Hydraulics Lab (CHL)
CSMART is developmental software that is updated frequently.
CSMART General Layout
CSMART is organized into a series of steps (see Figure 1) to guide the user in filtering the query, picking locations for analysis, and displaying the results. Step 1 is titled: Features. These are commercial tonnage, coast guard incidents, dredging, and other metrics which can be selected by the user. Step 2: Structures; allows the user to specify the structures to include in the analysis. The structures are organized by district. Step 3: Execute Query. Once all selections have been made the query is executed. Step 4: View Results. After completing the query CSMART ranks each of the structures selected in Step 2 according to each of the metrics chosen in Step 1 individually. A global ranking incorporating all the selected features and structures may also be executed during this step.
Step 1: Features
Step 1 prompts the user to select which features to include in the analysis. The features include: commercial tonnage, commercial fishing, coast guard incidents, dredging, cruise data, ferry data, boat ramps/marinas, binary choices, and structure condition ratings. These metrics are accessed via the sub-tabs as shown in Figure 2.
The user may select one or more of the sub-tabs for the analysis by clicking on the tab and checking the “Include?” box. Once a sub-tab has been selected the user can choose what data within each sub-tab to include in the query. For example, under the commercial tonnage sub-tab, selections for movement, year, and commodity are available. After all selections within a sub-tab are made the Save Filter Selections button must be pushed in order for the selections to be included in the analysis. The user may then move to other sub-tabs and make similar selections to filter the query.
Data for commercial tonnage, coast guard incidents, and dredging were obtained from the US Army Corps of Engineers (USACE) Navigation Data Center (http://www.ndc.iwr.usace.army.mil/index.htm). Commercial fishing data were taken from The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s National Marine Fisheries Service (NOAA-NMFS). Cruise data were obtained from the US Dept of Transportation’s Maritime Administration and Ferry data from Research and Innovative Technology Administration (RITA) Bureau of Transportation Statistics (BTS). Boat Ramp locations were from multiple sources. A nationwide database from EarthNC was supplemented by other sources for many individual coastal states. Binary choices allow the user to include structures that support a harbor of refuge, a subsistence harbor, public transportation, a military base, etc. These data come from project usage codes maintained by the Navigation Business Line at USACE-HQ. Finally, structure condition ratings were obtained from communications with district personnel. Commercial tonnage and cruise data are hard-linked to Corps structures, whereas the other data sets are spatially joined to selected structures by a user specified search radius. Figure 3 shows a one mile search radius around the East Arrowhead Breakwater in Cleveland. The red pins represent Coast Guard incidents, the yellow represent boat ramps and marinas, and the green represents dredging events that took place within the search radius.
Step 2: Structures
CSMART allows the user to select any of the Corps coastal structures for analyses and comparison. By clicking the Step 2: Structures Tab, a drop down tree organized into USACE districts appears. This tree is organized into a hierarchy containing districts, projects and individual structures. The user may click the small triangles to open the next level of the hierarchy. Structures may be chosen for analysis at each level in the tree by clicking the small box next to the desired selection. Once all selections have been made the user must push the Save Filter Selections button in order for the structures to be included in the analysis.
Step 3: Execute Query
Once all selections under steps one and two are completed selecting step 3 will execute the query. Depending on the users selections the query may take several seconds. Once complete the tab labeled Step 4: View Results will be visible.
Step 4: View Results
The results for each of the features selected in Step 1 are available to the user by clicking on the appropriate sub-tab under the View Results Tab. By selecting one of the sub-tabs CSMART will display each of the selected structures with its associated rank and data. Figure 5 shows the tonnage results of all the structures within CSMART for 2006 (Note: CSMART does not include local or internal traffic in tonnage totals). Notice that when a sub-tab is selected that was not included by the user a message is displayed saying the feature was not included in the analysis.
After looking at the results for a particular feature the user may want a more detailed look at a particular structure. In this case the user may click on the row containing the desired structure and a new sub-tab will appear with the structure name. Selecting the new sub-tab will show the user a more detailed breakdown of the particular feature for the selected structure. For example, by clicking the row corresponding to LA-LB Harbors San Pedro Breakwater, California under the tonnage sub-tab the data shown in Figure 6 is displayed.
In addition to ranking structures according to each feature individually a global ranking of structures incorporating all of the selected features may also be executed. By selecting the Global Ranking sub-tab the user may set a weight for each feature. The total of all the weights entered must be equal to one. By weighting each feature the user can specify how much he/she wants each feature to be counted toward the global ranking of the structures (see Figure 7).
Once all the weightings have been entered the user must click the Update Weightings button. Next the Global Rankings sub-tab may be selected, which will generate a table with a normalized ranking for each structure under each of the selected features. CSMART also computes an overall structure ranking and sorts the table accordingly. Figure 8 shows an example of the global rankings table.
The global rankings generated by CSMART are an initial screening of structures, not an in depth analysis of the structures that are most deserving of OM funding. The goal of CSMART is to assist OM decision makers in focusing their efforts on structures ranked by several general measures of significance.