Circular Basin: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
= Setup = | = Setup = | ||
The model is run to steady state from zero current and water level initial conditions with , , and both , and . Figure 1 shows the computational grid with 5 levels of refinement from 2000 m to 125 m. | [[Image:Grid_CB3.png|thumb|right|600px| Figure 1. Computational grid.]] | ||
The model is run to steady state from zero current and water level initial conditions with <math> W = 10^-4 m^2s^{-2}, , and both , and . Figure 1 shows the computational grid with 5 levels of refinement from 2000 m to 125 m. | |||
Revision as of 22:55, 11 May 2011
UNDER CONSTRUCTION
Analytical Solution
Dupont (2001) presented an analytical solution for a closed circular domain on an f-plane, with radius , a linear bottom friction, and a spatially variable wind stress equal to , where is the gradient of the wind forcing and is the vertical coordinate. The water surface elevation solution is given by
| (1) |
The current velocities are independent of the Coriolis parameter and are given by
| (2) |
| (3) |
Setup
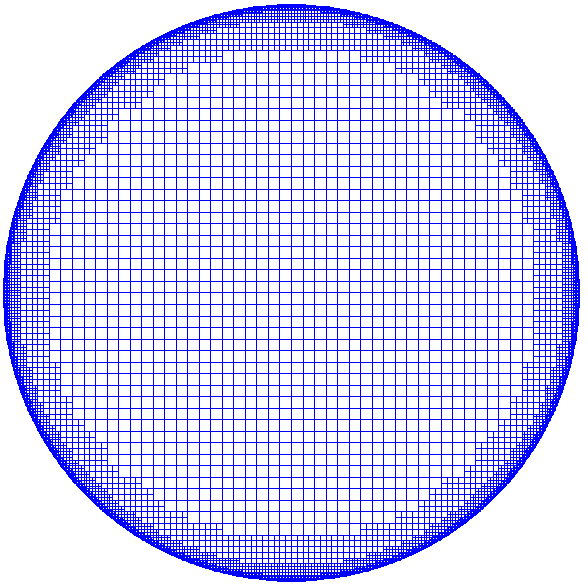
The model is run to steady state from zero current and water level initial conditions with <math> W = 10^-4 m^2s^{-2}, , and both , and . Figure 1 shows the computational grid with 5 levels of refinement from 2000 m to 125 m.
Results
Table 2. Goodness of fit statistics for the water elevation
| Statistic | Value |
| RMSE | 0.0074 m |
| RMAE | 0.0068 |
| R^2 | 0.991 |
| Bias | 0.0017 m |
References
- Dupont, F., 2001. Comparison of numerical methods for modelling ocean circulation in basins with irregular coasts. Ph.D. thesis, McGill University, Montreal.