Flow over a bump: Difference between revisions
| Line 41: | Line 41: | ||
Table 2. Goodness of fit statistics for the water elevation | Table 2. Goodness of fit statistics for the water elevation | ||
{|border="1" | {|border="1" | ||
|'''Statistic''' | |'''Statistic''' ||'''Value''' | ||
|'''Value''' | |||
|- | |- | ||
|RMSE | |RMSE || 0.0074 m | ||
| 0.0074 m | |||
|- | |- | ||
|RMAE | |RMAE || 0.0068 | ||
| 0.0068 | |||
|- | |- | ||
|R^2 | |R^2 || 0.991 | ||
| 0.991 | |||
|- | |- | ||
|Bias | |Bias || 0.0017 m | ||
| 0.0017 m | |||
|} | |} | ||
* For a definition of the goodness of fit statistics see [[Statistics | Goodness of fit statistics]]. | |||
<br style="clear:both" /> | <br style="clear:both" /> | ||
Revision as of 17:28, 1 June 2011
UNDER CONSTRUCTION
Setup
The spatial domain consists of a rectangular domain with the bed elevation given by
| (1) |
where is the horizontal distance.
Table 1. General Settings for Flow over a Bump
| Parameter | Value |
| Discharge | 0.18 m^3/s |
| Downstream water level | 0.33 m |
| Bottom friction | None |
Model Setup
The computational domain is 25 m long and has a constant grid resolution of 0.1 m. A flux boundary condition is specified at the inflow boundary and a constant water level boundary condition is applied to the downstream boundary. An adaptive time between 0.1-1 s is applied. The computational time on a single processor is approximately 1 min.
Results
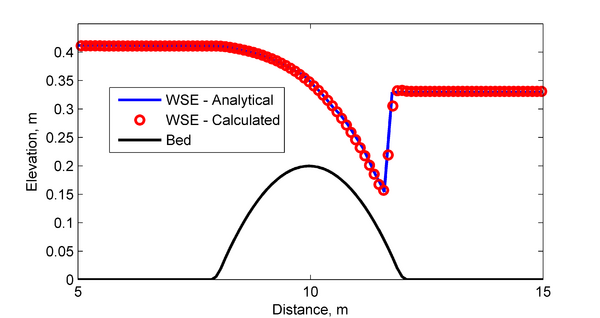
A comparison between the analytical solution for water levels is compared to the calculated water levels in Figure 2. As shown in the goodness of fit statistics, the model results agree well with the analytical solution. The minimum water level is captured well, however there is a small shift in the location of the water level drop over the bump toward the downstream direction.
Table 2. Goodness of fit statistics for the water elevation
| Statistic | Value |
| RMSE | 0.0074 m |
| RMAE | 0.0068 |
| R^2 | 0.991 |
| Bias | 0.0017 m |
- For a definition of the goodness of fit statistics see Goodness of fit statistics.
References
- Caleffi, V., Valiani, A., and Zanni, A. (2003). "Finite volume method for simulating extreme flood events in natural channels," Journal of Hydraulic Research, 41(2), 167-177.