Inlet Database: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 47: | Line 47: | ||
• Alaska (POA): Alaska | • Alaska (POA): Alaska | ||
• Hawaii (POH): Hawaii | • Hawaii (POH): Hawaii, U.S. Pacific Territories | ||
• Buffalo (LRB): New York, Ohio | • Buffalo (LRB): New York, Ohio | ||
Revision as of 17:03, 9 July 2011
Introduction
The U.S. Army Corps of Engineers' Coastal Inlets Research Program (CIRP) Federal Inlets database consolidates inlet characteristics and statistics in a conveniently accessible web-based form. The Federal Inlets Database contains information compiled for 156 Federally maintained inlets and entrances in the continental United States and Alaska. For the CIRP mission, an inlet or entrance is defined as a maintained channel connecting an ocean or lake to a smaller water body and which experiences long-period water motion by tide or seiching, together with a wave-induced longshore current. Inlet channels contribute to economic vitality as commercial navigational waterways, are part of the military infrastructure of the nation, and are key components of the estuarine ecosystem. The Corps maintains inlet navigability by dredging channels and through implementation and maintenance of controlling structures. Understanding the physical processes occurring at these inlets and entrances is required for predicting the evolution of the inlet and adjacent beaches, both under natural conditions and in response to engineering activities such as routine channel maintenance, channel deepening, and mining of ebb- and flood-tidal shoals.
The Federal Inlets Database presented here is in a developmental stage. A primary goal of the development of the database is to identify information gaps. The collection of additional data is necessary to fully populate the existing database. The Federal Inlets Database must ultimately function as a continually evolving information center to maintain accuracy with the recognition that inlet characteristics change through time. The Federal Inlets Database was organized with the goal of providing information on hydraulic, geomorphic, and geometric parameters for Federally maintained inlets within the continental United States and Alaska. Much of this information is not readily available at this time, and the CIRP is requesting assistance of those possessing additional information to complete the database.
Location
One motivation for the establishment of the Federal Inlets Database was to obtain information on many inlets over a diverse range of locations. Inlets within the United States have widely differing wave conditions, tidal prisms, magnitudes and directions of longshore sediment transport, structures, and physical geometries (as well as other parameters). The inlets contained within the database are located within 25 states and are maintained under the direction of 19 Corps Districts. The following is a listing of those managing District offices and the corresponding states containing inlets for which they are responsible.
• New England (NAE): Maine, New Hampshire, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, Connecticut
• New York (NAN): New York, New Jersey
• Philadelphia (NAP): New Jersey, Delaware
• Baltimore (NAB): Maryland
• Norfolk (NAO): Virginia
• Wilmington (SAW): North Carolina
• Charleston (SAC): South Carolina
• Savannah (SAS): Georgia
• Jacksonville (SAJ): Florida
• Mobile (SAM): Florida, Alabama
• New Orleans (MVN): Louisiana
• Galveston (SWG): Texas
• Los Angeles (SPL): California
• San Francisco (SPN): California
• Portland (NWP): Oregon, Washington
• Seattle (NWS): Washington
• Alaska (POA): Alaska
• Hawaii (POH): Hawaii, U.S. Pacific Territories
• Buffalo (LRB): New York, Ohio
• Detroit (LRE): Michigan, Wisconsin, Minnesota
The inlets contained within the Federal Inlets Database include those with one, two, or no jetties, are located along all coasts of the United States, and are of different sizes. Examples of the inlet conditions and locations include:







Sources of Parameters & Statistics
Geometric Properties
Aerial photographs and nautical charts were analyzed to evaluate the seaward and downdrift longshore extents of ebb tidal deltas for a number of the inlets within the database. Unrectified aerial photographs of different scales were consulted, with individual photograph scales determined through comparison of distance between two stationary objects, such as two jetties. On some photographs, the ebb delta could be identified through calm water. For other photographs, the location of the ebb delta had to be inferred by wave refraction and diffraction patterns (Gibeaut and Davis, 1993). Uncertainty is associated with the latter situation. If the ebb delta could not be readily identified, the photograph was eliminated from analysis. For some Pacific coast and highly wave-exposed Atlantic coasts, the location of the breaking waves for fair-weather waves is located landward of the terminal lobe of the ebb delta (due to their great depths), and therefore nautical charts were necessary for analysis.
Two geometric properties of the ebb-delta plan view shapes were obtained from interpreting the photographs or nautical charts: the distance to the most seaward extent of the ebb delta Ds, and the distance to the down-drift attachment bar Dd. Although measurements were made from one source for each inlet (most recent aerial photograph or nautical chart), several sources were reviewed for the inlet to ensure the determination was reliable. Uncertainties introduced for the distance measurements are estimated to be 25 to 150 m, depending on the scale, distortion, and parallax on the aerial photograph. Inlets selected for analysis were considered mature and assumed to be in equilibrium.
The distance to the most seaward extent of the ebb delta Ds was measured from the water-beach interface. In aerial photographs, this distance was determined visually based on the identification of the ebb delta through tonal changes (Gibeaut and Davis 1993). Nautical charts were analyzed if aerial photographs were not available or if ebb delta plan views were not distinguishable on photographs, e.g., at Pacific coast inlets with greater ebb shoal extents. Distance to the seaward extent of the ebb delta on nautical charts was determined as the point at which the contour lines were oriented similar to offshore contours far from the inlet (Vincent and Corson 1981). This distance was visually clear and easily identified by assessment of the slopes at the terminal lobe of the ebb delta. Gentle contours were identified over the ebb delta, transitioning to greater slopes as the ebb delta met the continental shelf.
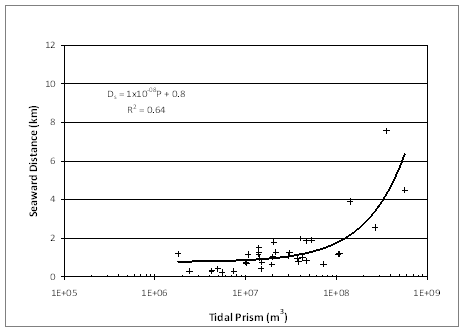
A consistent interpretation of the location of the shoreline from the aerial photographs and nautical charts was attempted. A baseline was determined with two end points located at the updrift and downdrift shorelines outside of the direct influence of the inlet or terminal structures. This methodology is similar to that of Gibeaut and Davis (1993), whose baseline end points were located where the ebb delta intersected the shoreline to obtain a shoreline trend from which their measurements could commence. Figure 2 shows an example of the shoreline trend utilized for measurement of the distance to the most seaward extent of the ebb delta. The identification of a baseline from which measurements are taken effectively eliminates ambiguity of an updrift and downdrift shoreline offset. For example, Grays Harbor, Washington, has a large shoreline offset (approximately 3 km), whereas Mason Inlet, North Carolina, has negligible offset. Shoreline offsets may be produced by coastal structures adjacent to the jetty or from the presence of the ebb delta attachment.
The distance to the downdrift attachment bar Dd was measured along a straight baseline set parallel to the trend of the shoreline. The measurement began at the downdrift inlet shoreline (at the narrowest section of the inlet channel) and ended at the location of the ebb delta attachment to the downdrift shoreline (Figure 8). If the location of the narrowest section of the inlet channel was not located along the baseline, then the measurement origin was translated perpendicularly to begin along the baseline. An attempt was made to determine a distance to the updrift attachment bar as done by Carr and Kraus (2001) for a limited number of inlets, but identification was difficult at most of the additional inlets examined. Updrift bypassing bars were found to be rare at inlets stabilized by jetties, so this parameter was not analyzed.
Data Verification
The data presented in the Federal Inlets Database was developed from sources within nineteen Corps Districts, from university and consulting industry reports, and from individuals conducting research at various tidal inlets throughout the study region.
Values presented in the database are representative. Many of the parameters reported, such as tidal prism, are not constant and vary over different time scales and in response to engineering activities such as dredging and dredge and fill. These values must be taken as estimates for the inlets.
Link to CIRP Website Inlet Database page: