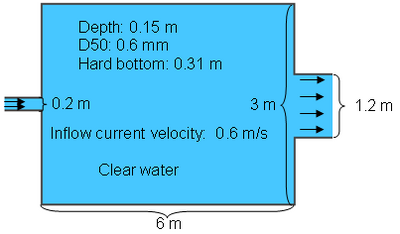
Clear water jet
Setup
The rectangular flume has a narrow 0.2 m-wide inlet and a 3 m-wide outlet. The initial water depth was 0.15 m with a 0.16 m layer of 0.6 mm sand over a concrete bottom. The flume was 5 m long and 4 m wide. The measured sand settling velocity of 0.013 m/s was used. The computational mesh consisted of 62 rows and 69 columns (Figure 2). The computational time was 30 seconds. The transport equation which best fit the measurements was the Soulsby-van Rijn (1997). The bed and suspended load transport scaling factors were calibrated to 2.0 which is within the acceptable range for the transport formula scatter.
The experiment consist of a trapezoidal channel of uniform find sand (d50 = 0.16 mm) with a steady flow (0.51 m/sec) perpendicular to the channel axis (Gallappatti and Vreugdenhil 1985). The water depth on the upstream bank is about 0.39 m. Three bank slopes were tested: 1:3, 1:7, and 1:10. A flux boundary condition was used at the inlet and a water level boundary condition at the outlet. A constant Manning n coefficient of 0.025 (default) was used. The Lund-CIRP transport formula was used for all three test cases. The morphologic scaling factor was set to 1.0. The adaptation length was calibrated to be 0.6 m.
Results
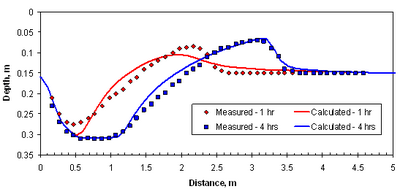
The figures below show a comparison between measured and computed bed elevations.

References
Soulsby, R. (1997) "Dynamics of marine sands" Thomas Telford Publications, London, ISBN 0 7277 2584 X.
Thuc, T. (1991) “Two-dimensional morphological computations near hydraulic structures”, Doctoral Dissertation, Asian Institute of Technology, Bangkok, Thailand.