GenCade
GenCade
POCs: Ashley Frey <br\>Ashley.E.Frey@usace.army.mil <br\>601-634-2006 <br\>US Army Engineer Research and Development Center (ERDC) <br\>Coastal and Hydraulics Lab (CHL)
<br\>Nick Kraus <br\>Nicholas.C.Kraus@usace.army.mil <br\>601-634-2016 <br\>US Army Engineer Research and Development Center (ERDC) <br\>Coastal and Hydraulics Lab (CHL)
GenCade is a 1D model that combines GENESIS with Cascade. It is operated within the Surface-water Modeling System (SMS) interface. The first open release of GenCade is expected to occur in December 2010. A user guide, examples of simple cases, and applications will be posted here.
User Guide
Getting Started
This GenCade guide was developed in September 2010. Most of the screenshots used in this guide were created with the July 29, 2010, build of the SMS. The August 25, 2010, build was used to create the screenshots for the Developing Alternatives and Time-dependent Wave Transmission sections. This guide refers to GenCade_v1_066.exe as the most recent executable. Developers are constantly upgrading the SMS and GenCade executables, so a future version may look slightly different from this user guide.
Setup GenCade in the SMS
GenCade is one model available in the SMS (Surface-water Modeling System) interface. To use GenCade, a working version of SMS 10.1 and executable for SMS 11.0 Development are necessary. The SMS 11.0 Development executable is copyrighted, so a registration code is necessary before using.
First, locate the GenCade executable on your machine. Drop the executable into the models folder under SMS 10.1 as shown in Figure 1.
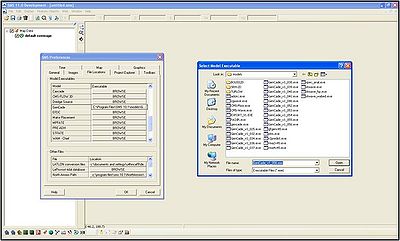
Once again, the capabilities of GenCade are only available in SMS 11.0 Development. If SMS 10.1 is already installed on the computer and a registration code for SMS 11.0 Development has been obtained, simply drag the SMS 11.0 executable into the SMS 10.1 folder (most likely in Program Files). Double-click on the SMS 11.0 executable to open SMS 11.0 Development. At this time, a prompt will open asking for the registration code. Before beginning to work in GenCade, go to Edit->Preferences. Select the tab File Locations and scroll down to GenCade under Model Executables. Click the button under Executable located directly to the right of GenCade. If GenCade has not been used previously, the button will most likely say BROWSE. After selecting this button, find the latest GenCade executable on the computer and select. The row to the right will specify the location of the executable which will be used to run GenCade (Figure 2).
Set the current projection
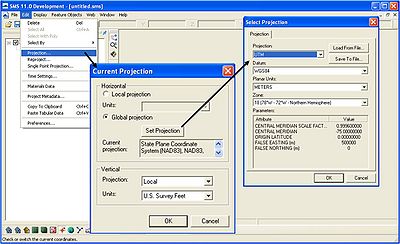
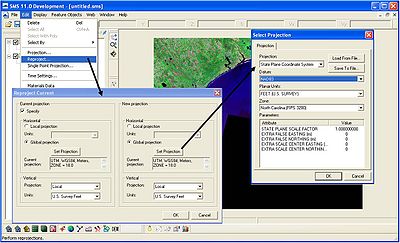
GenCade uses a real world coordinate system, so it is necessary to set up the current projection upon opening the SMS. Aerial photos, shorelines, and other georeferenced files can be opened in the SMS. Go to Edit->Projection and define the current projection (Figure 3). This will ensure all shorelines, structures, wave gages, and other important features are mapped correctly.
Reproject current projection
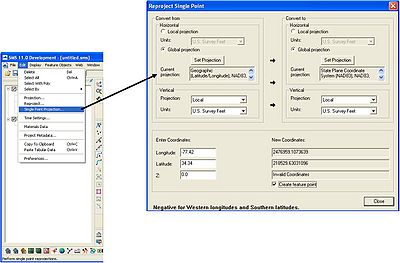
In some cases, the shorelines and the aerial photo may be in different coordinate systems. To change the projection, go to Edit->Reproject. A new window will open where the current projection and new projection can be specified (Figure 4).
Preparing Input Files
Initial shoreline
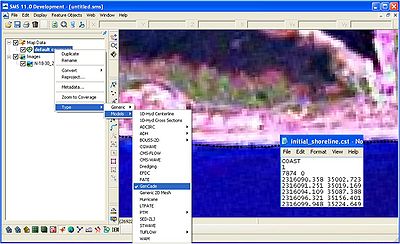
Before dragging a file into the SMS interface, right click on default coverage under Map Data in the left panel. Select Type->Models->GenCade. To bring in a shoreline or regional contour as a *.cst, the original text file must be modified. See Figure 5 for the required format. The first number in the third row represents the number of points in the file. The other numbers in the first three rows will remain the same.
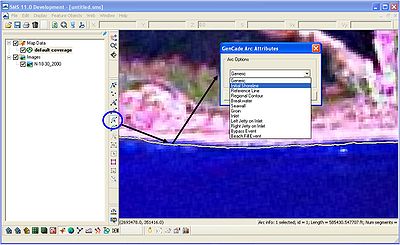
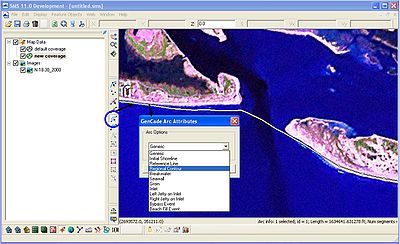
Once the shoreline is represented in the interface, click the Select Feature Arc button and double-click on the shoreline. The GenCade Arc Attributes will open. Select Initial Shoreline and click OK (Figure 6). Now the shoreline is defined.
Regional contour or additional shorelines
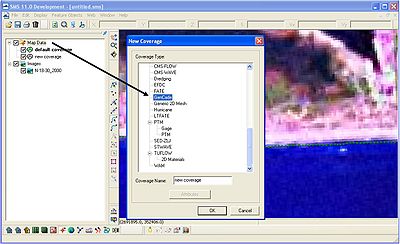
In some cases, it may be necessary to include a regional contour or additional shorelines. Right-click on Map Data and select New Coverage. A window will open; scroll down and select GenCade as the coverage type (Figure 7). Open the regional contour in the interface, and click on the Select Feature Arc button. After double-clicking on the regional contour, select Regional Contour as the Arc Option in the GenCade Arc Attributes window (Figure 8). Additional shorelines can be added in a similar fashion.
Merge coverages
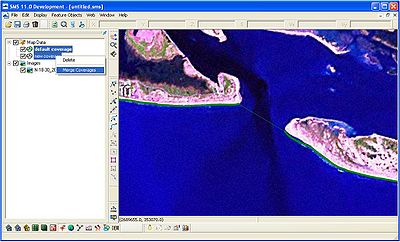
After the initial shoreline and regional contour have been loaded and defined in the SMS interface, it is necessary to merge the two lines in a single coverage. All structures, inlets, wave gages, and other features will be created in this single coverage. Highlight both the default coverage (initial shoreline) and the new coverage (regional contour). Right-click and select Merge Coverages (Figure 9). A window will open asking "Do you want to delete the coverages used to make the merged coverage?" By selecting no, the initial shoreline and regional contour will remain in the interface and if a problem occurs, these coverages can be merged again. It may be necessary to redefine the shoreline and regional contour in this new coverage.
Grid Setup
Orientation and cell size
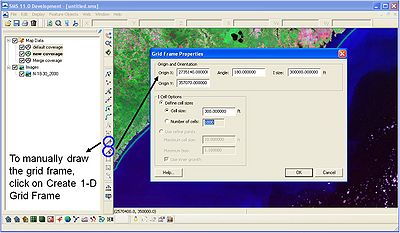
After merging the shoreline and regional contour into one coverage, the grid can be setup. If the user knows the what length grid to use, it is advisable to do this before adding any features to coverage. To manually draw the grid frame, click on the Create 2-D Grid Frame. The GenCade grid frame will be purple and have an arrow at one end. If a person was walking down the grid to the arrow, the water would be to the left and the land would be to the right. For example, if the GenCade grid arrow was pointing south, the water would be to the east (left) and the land would be to the west (right). The grid can be modified by clicking the Select 1-D Grid Frame and double-clicking on the square in the center of the purple grid line. The Grid Frame Properties window will open, and the Origin X, Origin Y, Angle, and I size can be modified (Figure 10). The I size is the length of the grid. The cell size can be constant or variable. If the user chooses to change the cell size under define cell sizes, the number of cells will change accordingly.
Inlets, shoals, jetties, and dredging
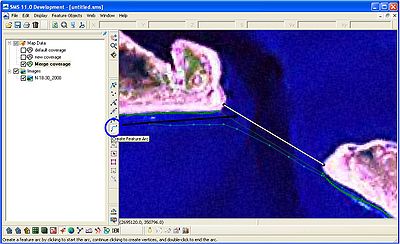
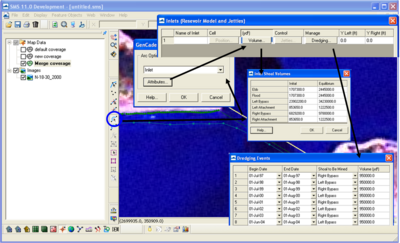
To create an inlet, select the Create Feature Arc button and draw a line from one side of the inlet to the other (Figure 11). This is why it is helpful to have a high quality aerial in the background. Once the inlet is drawn, click on the Select Feature Arc button and double-click on the line representing the inlet. The GenCade Arc Attributes window will open. Select Inlet and click on Attributes. This will open the Inlet Reservoir Model window. The inlet can be named, shoal volumes defined, and dredging added. Click on the Volume button to add the initial and equilibrium shoal volumes for the ebb, flood, left bypass, left attachment, right bypass, and right attachment. Similarly, in the dredging window, the user can define the beginning date, the ending date, the volume, and the shoal to be mined (Figure 12). After clicking OK, the line representing the inlet will turn blue.
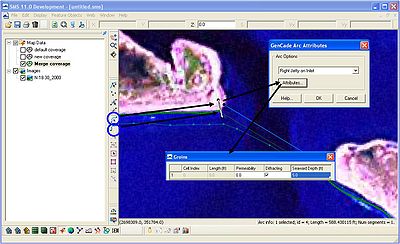
A jetty can be drawn at the inlet after selecting the Create Feature Arc button. After drawing the jetty, click on the Select Feature Arc and double-click on the line representing the jetty. When the GenCade Arc Attributes window opens, select either Left Jetty on Inlet or Right Jetty on Inlet (remember the left jetty is to the left of a person standing on land) and click on Attributes. A new window will open where user can choose the permeability, select diffracting or non-diffracting, and include a seaward depth (Figure 13). The line representing a jetty will also turn blue.
Beach fills
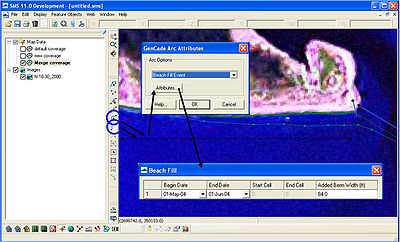
Beach fills can be drawn in the same way as inlets. Select the Create Feature Arc button to draw the beach fill. Beach fills can be drawn directly on the shoreline or slightly offshore. If there are many beach fills in one location during the simulation, each beach fill should be placed slightly offshore so they do not overlap. After each beach fill is drawn, click on the Select Feature Arc and double-click on the line representing the beach fill. Select the Beach Fill Event after the GenCade Arc Attributes window opens. For each beach fill, add the starting and end dates and the added berm width (Figure 14). After selecting OK in the GenCade Arc Attributes window, the line representing the beach fill will turn green.
Groins
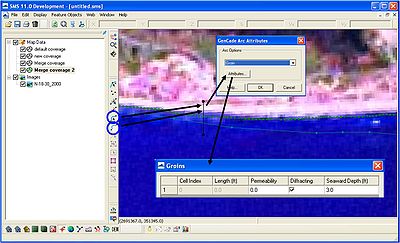
Once the location for a groin is chosen, select the Create Feature Arc button. In most cases, the arc representing the groin will cross the regional contour and initial shoreline. Do not draw either end of the groin near the regional contour or initial shoreline. When this occurs, the node from the groin will connect to the initial shoreline or regional contour. This will divide the regional contour or initial shoreline into two separate arcs, where only one of the arc will be considered the regional contour or initial shoreline. At this point, GenCade does not have the capability to identify multiple arcs for the initial shoreline or regional contour. The best way to prevent this (at this time) is to save often, reopen the project, and start at the step previously saved. After drawing the feature arc for the groin, click on the Select Feature Arc button. The GenCade Arc Attributes window will open. Select groin in the Arc Options menu and click on Attributes. The window for groins includes the permeability and seaward depth (in the user specified units). The user may also decide "Diffracting" or "Non-diffracting" for the groin.
Wave Data
There are several ways to represent wave gages in the conceptual model. If the coordinates for the wave gages are in the same coordinate system as the conceptual model, it is very easy to bring in the location of the gages. Drag the file with the coordinates representing the wave gages into the SMS interface. The Open File Format window will open. Select Use Import Wizard and click OK. Follow the direction for the File Import Wizard and select OK. The wave gage locations will be represented as scatter data. Simply select the Create Feature Point button in the conceptual model and draw a feature point directly on top of each point. Now the wave gage locations are represented in the model.
If the coordinates for the wave gages are in a different coordinate system than the GenCade conceptual model, the process to bring in the locations representing the gages is slightly different. Go to Single Point Projection under the Edit menu. The Reproject Single Point window will open. In the Convert from window, choose the projection of the wave gage. In the Convert to window, specify the projection of the GenCade conceptual model. At the bottom of the window, enter the coordinates of the wave gage and check create feature point. Once the window is closed, the location of the wave gage will become a feature point in the GenCade conceptual model. This process will need to be repeated for each wave gage.
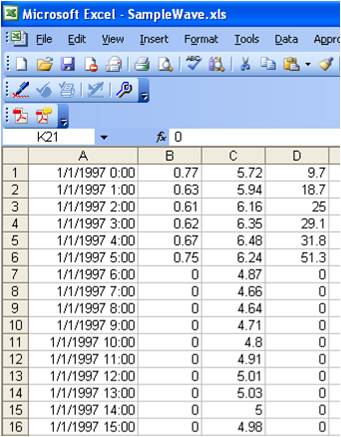
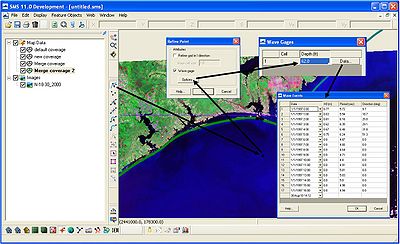
Once the wave gages are represented in the conceptual model as feature points, click on the Select Feature Point button and double click on the point representing the wave gage. In the Refine Point window, check wave gage and click on options. The wave gages window will open and the user can specify the depth of the wave gage. After clicking Data, the Wave Events window will open. There are four columns in this window: Date (month, day, year, and time), Ho (the wave height is always in meters), Period (in seconds), and Direction (in degrees). The direction is shore (grid) normal. In most cases, the user will need to convert to grid normal outside of the SMS interface. It is expected that the ability to input wave data in meteorological, oceanographic, or local coordinates will added to the SMS interface during this FY.
For the SMS to read the wave information correctly, the information must be copied and pasted in a specific format. The easiest way to do this is to bring the wave information into Microsoft Excel. The first column will include the month, day, year, and time. The date must be in the format of 1/1/1997 0:00. The wave height, period, and direction are included in the proper column. An example of this format is shown in Figure 18. Before copying the wave information to GenCade in the SMS interface, the user must clean the information. Since the waves are read in as shore (grid) normal, the wave direction must be between -90 and +90 degrees. If wave direction is coming from shore in the raw wave data, it is necessary to make the wave height and direction zero for GenCade.