CMS-Flow:Tech Report 3
__notitle__
Coastal Modeling System
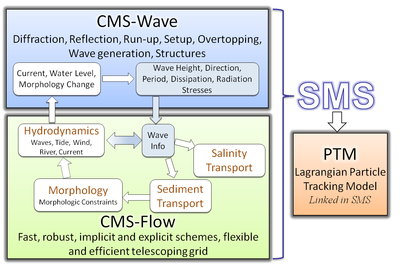
Introduction The Coastal Modeling System (CMS) is an integrated numerical modeling system for simulating nearshore waves, currents, water levels, sediment transport, and morphology change (Militello et al. 2004; Buttolph et al. 2006a; Lin et al. 2008; Reed et al. 2011). The system is designed for coastal inlets and navigation applications including channel performance and sediment exchange between inlets and adjacent beaches. Modeling provides planners and engineers essential information for improving the usage of USACE Operation and Maintenance Funds. CIRP is developing, testing, improving and transferring the CMS to Corps Districts and industry and assisting users in engineering studies. The overall framework of the CMS and its components are presented in Figure 1.
- Background
- Key Features
- Fully integrated system
- Finite Volume Method - Mass conservative
- Non-uniform Cartesian Grid - Easy to setup and run
- Telescoping Cartesian Grid - Flexible, efficient, and easier to generate than unstructured meshes
- Supports most common types of forcing and boundary conditions
- Robust numerical schemes for reliable, crash-free simulations
- Parallelization on desktop computers for fast computation
- User-friendly interface
System Components
CMS-Flow is a coupled hydrodynamic and sediment transport model capable of simating depth-averaged circulation, salinity and sediment transport due to tides, wind and waves. The hydrodynamic model sovles the conservative form of the shallow water equations and includes terms for the Coriolis force, wind stress, wave stress, bottom stress, vegetation flow drag, bottom and friction, and turbulent diffusion. There are three sediment transport models available in CMS: a sediment mass balance model, an equilibrium advection diffusion model, and non-equilibrium advection-diffusion model. The salinity transport is simulated with the standard advection diffusion model and includes evaporation and precipitaion. All equations are solved using the Finite Volume Method on a non-uniform Cartesian grid. For additional information on CMS-Flow visit CMS-Flow Main Page.
The CMS-Wave is a spectral wave transformation model and solves the steady-state wave-action balance equation on a non-uniform Cartesian grid. It considers wind wave generation and growth, diffraction, reflection, dissipation due to bottom friction, whitecapping and breaking, wave-wave and wave-current interactions, wave runup, wave setup, and wave transmission through structures. For additional information information on CMS-Wave visit CMS-Wave Main Page.