CMS-Flow Bottom Friction: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 38: | Line 38: | ||
To interpolate bottom roughness data from a scatter set | To interpolate bottom roughness data from a scatter set | ||
<br style="clear:both" /> | |||
=== Exporting === | === Exporting === | ||
Exporting the bottom roughness (friction) datasets is useful for creating different project alternatives or when switching from different bottom roughness datasets types such as from ''Manning's n'' to ''Bottom Friction Coefficient'' and back. It is also useful for scripting multiple runs with different project alternatives. | |||
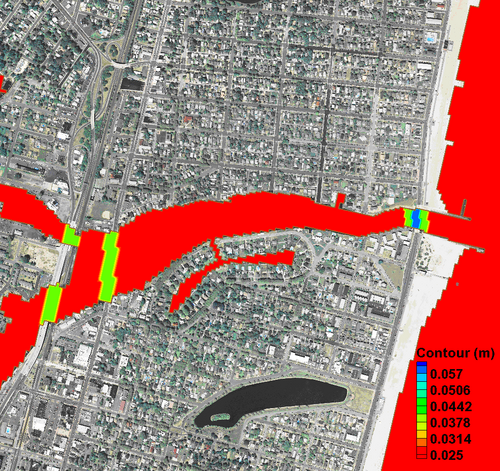
[[Image:Export_BottomFrictCoef.png|thumb|left|500px||Figure 5. Manning n contours after modifying the areas under all three bridges.]] | |||
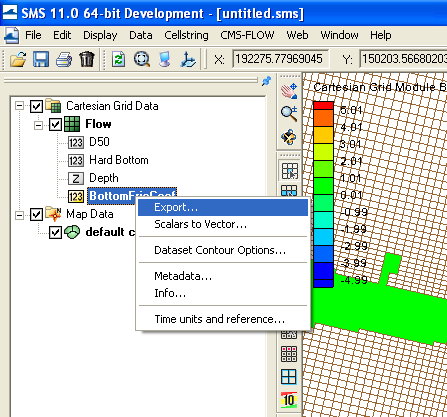
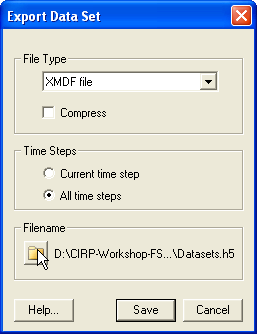
[[Image:Export_Data_Set.png|thumb|none|400px||Figure 6. Exporting the ''Bottom Friction Coefficient'' to an XMDF file.]] | |||
[[Image: | |||
<br style="clear:both" /> | |||
=== Advanced Cards === | === Advanced Cards === | ||
'''Table 2. Advanced Cards related to the bottom friction (roughness) dataset''' | '''Table 2. Advanced Cards related to the bottom friction (roughness) dataset''' | ||
| Line 58: | Line 59: | ||
<br style="clear:both" /> | <br style="clear:both" /> | ||
== Wall | == Wall Friction == | ||
[[Image:Wall_friction.png|thumb|none|400px||Figure 6. Wall friction specification in the ''CMS-Flow Model Control'' window.]] | |||
The wall friction enhances the flow drag perpendicular to any dry boundary. The wall friction may be turned ''On'' or ''Off'' in the ''Flow'' tab of the ''CMS-Flow Model Control'' window (see Figure 7). The default in SMS is for the wall friction to be ''ON''. Table 2 shows the CMS card used activating the wall friction. | |||
'''Table 2. SMS Cards related to the bottom friction datasets''' | |||
{| border="1" | |||
! Card !! Arguments !! Default !! Range !! Description !! Versions | |||
|- | |||
| USE_WALL_FRICTION || CHARACTER || ON || ON <nowiki>|</nowiki> OFF || Turns on or off wall friction || >=3.5 | |||
|} | |||
<br style="clear:both" /> | <br style="clear:both" /> | ||
Revision as of 19:33, 17 January 2011
Overview
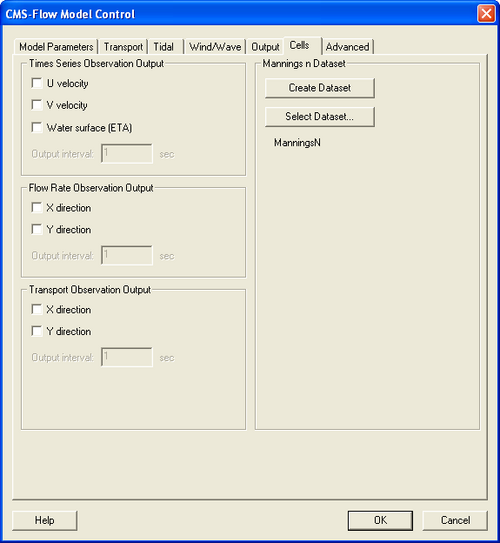
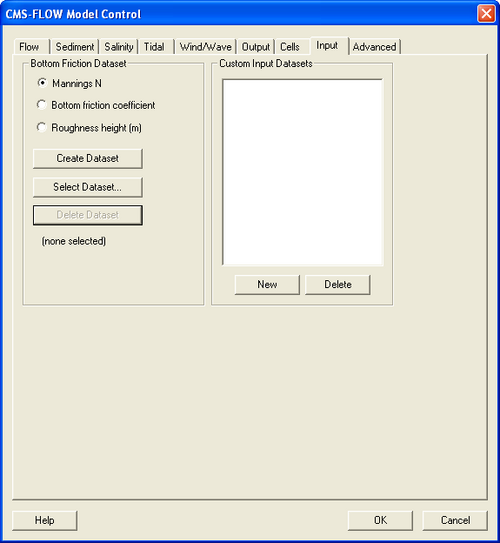
In SMS versions 10.1 and earlier, the bottom roughness is specified using the Manning's n coefficient in the Cells tab of the CMS-Flow Model Control window (see Figure 1). In SMS 11.0, the option is provided to use a roughness height, or bottom friction coefficient in addition to the Manning's coefficient. In SMS 11.0 the bottom roughness is specified in the Bottom Friction Dataset section of within the Input tab of the CMS-Flow Model Control window (see Figure 2). The Bottom Friction Dataset is specified at every computational (ocean) cell and is required for each model simulation.
Bottom Friction Dataset
Creating
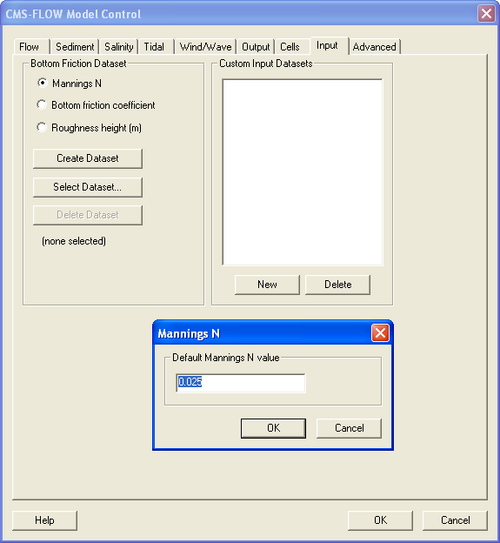
In SMS 11.0 each time a new CMS-Flow simulation is created a bottom friction (roughness) dataset needs to be created using the Create Dataset button. The bottom friction parameter (related to Manning ) is spatially varying (cell-specific) over the grid domain. The default value upon grid creation is 0.025. At times a user may desire to represent locations where added friction is needed due to structures or increased turbulence due to sharp changes in current speed. More information on using this feature of CMS-Flow can be found here.
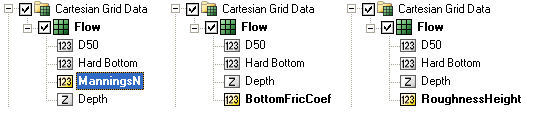
Once the Bottom Friction Dataset is created and the CMS-Flow Model Control window closed, a new auxiliary dataset will appear in the SMS Project Explorer (see Figure 3). Table 1. shows a list of the CMS cards related to the bottom friction datasets.
Table 1. SMS Cards related to the bottom friction datasets
| Card | Arguments | Default | Range | Description | Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| USE_WALL_FRICTION | CHARACTER | ON | ON | OFF | Turns on or off wall friction | >=3.5 |
| MANNING_N_DATASET | CHARACTER CHARACTER | [<grid file>] [<grid name>//"Datasets/ManningsN"] | none | Grid file name and dataset path for the input Manning's n dataset | >=v3.5 |
| BOTTOM_FRICTION_COEF_DATASET | CHARACTER CHARACTER | [<grid file>] [<grid name>//"Datasets/BottomFricCoef"] | none | Grid file name and dataset path for the input bottom friction coefficient dataset | >=v4.0 |
| ROUGHNESS_HEIGHT_DATASET | CHARACTER CHARACTER | [<grid file>] [<grid name>//"Datasets/RoughnessHeight"] | none | Grid file name and dataset path for the input roughness height dataset | >=v4.0 |
Editing
Bottom roughness datasets may be edited manually, using the Data Calculator or by interpolating from a scatter set. Figure 4 shows an example where the Manning's n coefficient is increased for Shark River Inlet to account for the presence of vertical piles.
To interpolate bottom roughness data from a scatter set
Exporting
Exporting the bottom roughness (friction) datasets is useful for creating different project alternatives or when switching from different bottom roughness datasets types such as from Manning's n to Bottom Friction Coefficient and back. It is also useful for scripting multiple runs with different project alternatives.
Advanced Cards
Table 2. Advanced Cards related to the bottom friction (roughness) dataset
| Card | Arguments | Default | Range | Description | CMS Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MANNING_N_CONSTANT | real number | none | >=0.0 | Specifies a constant input Manning's n coefficient. Over-rides any previous bottom friction cards. | >=v4.0 |
| BOTTOM_FRICTION_COEF_CONSTANT | real number | none | >=0.0 | Specifies a constant input Bottom Friction Coefficient. Over-rides any previous bottom friction cards. | >=v4.0 |
| ROUGHNESS_HEIGHT_CONSTANT | real number | none | >=0.0 | Specifies a constant Roughness Height in m. Over-rides any previous bottom friction cards. | >=v4.0 |
Wall Friction
The wall friction enhances the flow drag perpendicular to any dry boundary. The wall friction may be turned On or Off in the Flow tab of the CMS-Flow Model Control window (see Figure 7). The default in SMS is for the wall friction to be ON. Table 2 shows the CMS card used activating the wall friction.
Table 2. SMS Cards related to the bottom friction datasets
| Card | Arguments | Default | Range | Description | Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| USE_WALL_FRICTION | CHARACTER | ON | ON | OFF | Turns on or off wall friction | >=3.5 |
Advanced Features
Wave-enhanced Bottom Friction
Table 2. Advanced Cards related to the bottom friction
| Card | Arguments | Default | Range | Description | CMS Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WAVE-CURRENT_MEAN_STRESS | character | W09 | W09 | DATA2 | DATA13 | F85 | HT95 | Defines the model used for calculating the mean bottom shear stress used in hydro | >=4.0 |
Bed Slope Friction Factor
Table 2. Advanced Cards related to the bottom friction
| Card | Arguments | Default | Range | Description | CMS Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BED_SLOPE_FRICTION_FACTOR | character | OFF | ON| OFF | Specifies whether to include the bed slope friction factor or not in the calculation of the bed friction | >=4.0 |