Flow over a bump: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(→Setup) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
\end{cases} </math> |2=1}} | \end{cases} </math> |2=1}} | ||
where <math> | where <math>z_b</math> is the bed elevation and <math>x</math> is the horizontal distance. | ||
== Model Setup == | == Model Setup == | ||
A computational grid with constant water depth of 5 m and irregular boundaries is used in order to test the model performance. The computational grid has 60 columns and 70 rows and a constant resolution of 500 m. | A computational grid with constant water depth of 5 m and irregular boundaries is used in order to test the model performance. The computational grid has 60 columns and 70 rows and a constant resolution of 500 m. | ||
[[Image:Bump_Grid.png|thumb|left|600px| Figure 1. Computational grid.]] | |||
<br style="clear:both" /> | |||
== | == Results == | ||
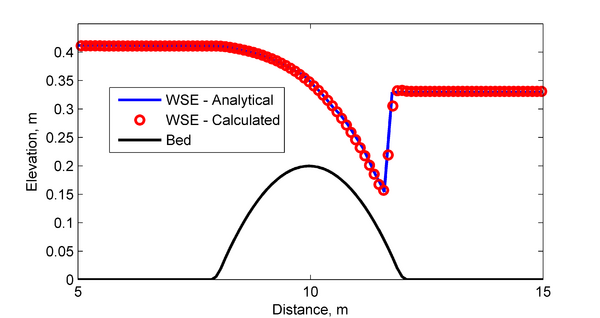
[[Image: | [[Image:Bump_Results.png|thumb|left|600px| Figure 2. Comparison of analytical and calculated water surface elevations and bed elevations.]] | ||
<br style="clear:both" /> | <br style="clear:both" /> | ||
Revision as of 23:19, 14 December 2010
UNDER CONSTRUCTION
Setup
The spatial domain consists of a rectangular
| (1) |
where is the bed elevation and is the horizontal distance.
Model Setup
A computational grid with constant water depth of 5 m and irregular boundaries is used in order to test the model performance. The computational grid has 60 columns and 70 rows and a constant resolution of 500 m.
Results