CMS-Flow:Structures: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
<br style="clear:both" /> | <br style="clear:both" /> | ||
* [[Weirs]] | * [[Weirs]] [[File:Weirs_Figure_6.png|thumb|left|600px|Figure 6. CMS simulation velocity patterns for Case 3.]] | ||
<br style="clear:both" /> | |||
* [[Culverts]] | * [[Culverts]] | ||
Revision as of 17:31, 19 September 2010
Structures in CMS
- Rubble Mounds
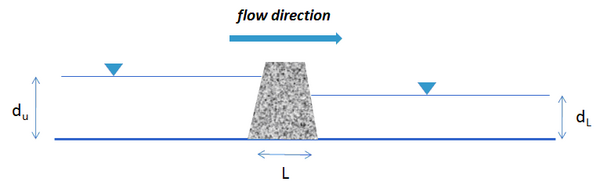
Schematic of the model configuration for validation and numerical grid independence test.
- Rubble mound structures are a common coastal engineering structure used for shoreline protection and flow and sediment transport control. They are typically used as seawalls, groins, breakwaters and jetties. The design of rubble mound structures often consists of a core of small to medium size rock or riprap covered with larger rock or riprap to armor against wave energy. In coastal modeling, it is usually reasonable to assume that the flow through these structures is negligible, and they are represented as solid structures, impermeable to both flow and sediment transport. However, some rubble mounds such as that of Dana Point, CA are designed with a sufficiently large diameter core material to allow for flow and fine sediments to pass through and coarser sediment to be trapped within.
- Weirs

Figure 6. CMS simulation velocity patterns for Case 3.