CMS-Flow Model Parameters: Difference between revisions
| Line 45: | Line 45: | ||
There are several situations where it is convenient to specify a user defined hot start file. For example, if the user forgets to setup the model output a hot start file or when running steady state conditions. A hot start file can easily be created and exported by the user from the SMS interface. The model requires at water levels, current velocities, concentrations, and water depths. Any datasets that are missing from the initial file. It is important to note that the names and paths of the initial condition datasets is important. | There are several situations where it is convenient to specify a user defined hot start file. For example, if the user forgets to setup the model output a hot start file or when running steady state conditions. A hot start file can easily be created and exported by the user from the SMS interface. The model requires at water levels, current velocities, concentrations, and water depths. Any datasets that are missing from the initial file. It is important to note that the names and paths of the initial condition datasets is important. | ||
'''Table 2. Path and name for initial condition file variables.''' | |||
{| border="1" | {| border="1" | ||
! Variable !! Path and Name | ! Variable !! Path and Name | ||
| Line 70: | Line 70: | ||
[[Image:Hot_Explorting_User_Defined_Arrows.png|thumb|right|500px| Figure 4. Dataset Toolbox showing a time step sample of the water elevation and current velocity datasets for use in a hot start (initial condition) file.]] | [[Image:Hot_Explorting_User_Defined_Arrows.png|thumb|right|500px| Figure 4. Dataset Toolbox showing a time step sample of the water elevation and current velocity datasets for use in a hot start (initial condition) file.]] | ||
<br style="clear:both" /> | <br style="clear:both" /> | ||
'''Table 3. CMS-Flow card for specifying the initial condition file.''' | |||
{| border="1" | {| border="1" | ||
! Card !! Arguments !! Default !! Range !! Description | ! Card !! Arguments !! Default !! Range !! Description | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | INITIAL_STARTUP_FILE || CHARACTER || none || none || Julian data in YYDDD with YY being last two digits of the year, and DDD the Julian day of the year. | ||
|} | |} | ||
<br style="clear:both" /> | <br style="clear:both" /> | ||
Revision as of 00:41, 19 January 2011
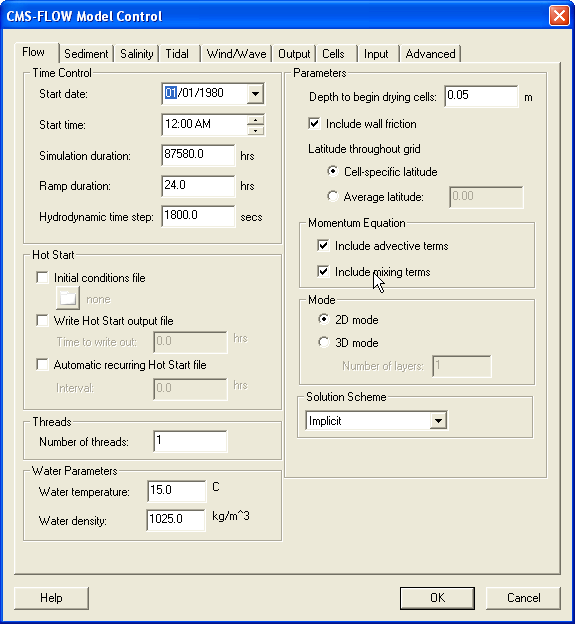
All of the CMS-Flow model parameters, settings, and output options are controlled from the CMS-Flow Model Control window (Figure 1). The window has several tabs including the Flow tab in which most of the general settings are set for CMS-Flow. To open the CMS-Flow Model Control window, click on CMS-Flow | Model Control. The first tab will be the Flow tab. There are several sections within the tab including Time Control and Hot Start options.
Time Control
Below are some of the CMS cards related to the Time Control of the Flow tab. Table 1 provides a brief description of the CMS cards used for time control.
| Card | Arguments | Default | Range | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| STARTING_JDATE | REAL | none | none | Julian data in YYDDD with YY being last two digits of the year, and DDD the Julian day of the year. |
| STARTING_JDATE_HOUR | REAL | none | none | Julian hour . |
| HYDRO_TIME_STEP | REAL | Calculated based on solution scheme and courant number | none | Sets to the time step for hydrodynamics in seconds. |
| DURATION_RUN | REAL | 48.0 | >RAMP>0 | Sets the duration of the model simulation in hours. |
| DURATION_RAMP | REAL | 1.0 | Sets the length of the ramp period in which the model forcing is slowly ramped from zero. |
Hot Start
The term Hot start refers to starting a simulation with an initial condition other zero (cold start). Hot starts are used for specifying initial conditions or restarting simulations at intermediate times. The hot start controls are set in the Flow tab of the CMS-Flow Model Control window.
Hot Start File
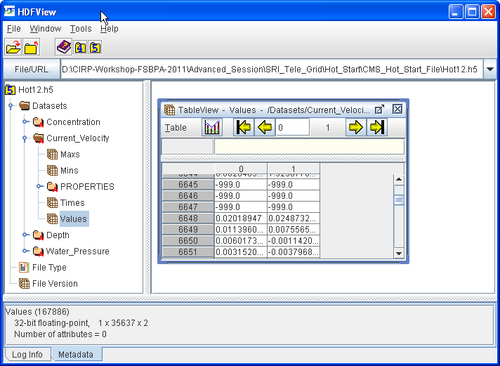
The CMS hot start feature CMS lets the user restart simulations that have been stopped due to electric outages, hardware malfunctions, or model crashes. In the case of a model crash the user, may restart the model using larger solver iterations and/or time steps to stabilize the simulation. The user has the option to specify a hot start output time or an interval for outputting a recurring hot start file. Every time the hot start file is written, it overwrites the previous information. The CMS Hot Start file saves information on the water elevation (pressure), and current velocities. If the sediment transport is active, then the water depth, and sediment concentrations are also saved for each size class. The CMS hot start file is a binary XMDF file, has the name Hot_Start.h5 and is saved in the directory of the CMS-Flow files. Figure 1 shows the structure of the hot start file. After saving a CMS Hot Start file, it is a good idea to rename the file with a different name before using it as an initial conditions file. This way, the file will not be overwritten in future simulations.
Table 1. Hot Start CMS-Flow Cards
| Card | Arguments | Default | Range | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HOT_START_OUTPUT_FILE | CHARACTER | none | none | Julian hour. |
| HOT_START_TIME | REAL | none | none | Sets the hot start output time. |
| AUTO_HOT_START_INTERVAL | REAL | none | none | Sets the recurring hot start output time. |
Initial Conditions File
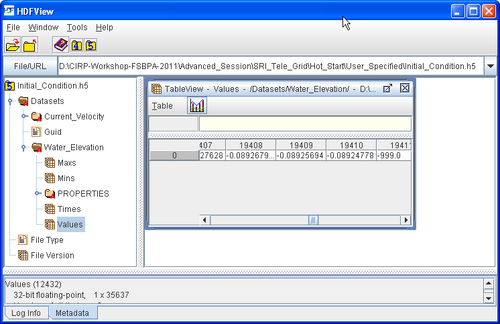
There are several situations where it is convenient to specify a user defined hot start file. For example, if the user forgets to setup the model output a hot start file or when running steady state conditions. A hot start file can easily be created and exported by the user from the SMS interface. The model requires at water levels, current velocities, concentrations, and water depths. Any datasets that are missing from the initial file. It is important to note that the names and paths of the initial condition datasets is important.
Table 2. Path and name for initial condition file variables.
| Variable | Path and Name |
|---|---|
| Water surface elevation | Datasets\Water_Elevation |
| Current velocity | Datasets\Current_Velocity |
| Sediment concentrations | Datasets\Concentration |
| Salinity concentrations | Datasets\Salinity |
The steps for creating a user defined hot start or initial condition file from a CMS-Flow solution file are outlined below.
- Import CMS-Flow grid and solution file.
- Sample a time step of the solution datasets for use in the initial condition
- Click on Data | Data Calculator
- Under the Tools section, select Sample time steps.
- Under the Datasets section, click on the Water Elevation
- Click on Data | Data Calculator
- Export the initial condition datasets to an XMDF file
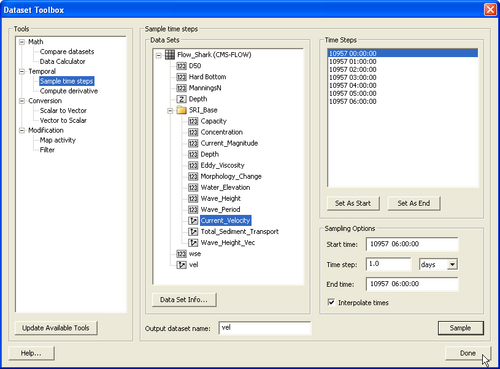
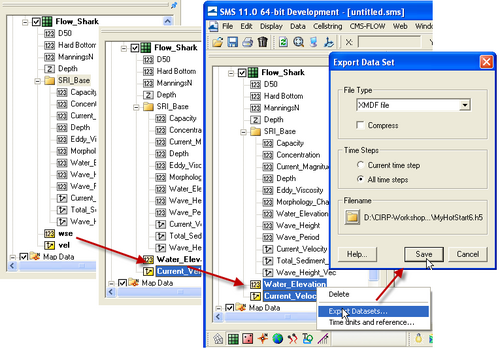
Table 3. CMS-Flow card for specifying the initial condition file.
| Card | Arguments | Default | Range | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| INITIAL_STARTUP_FILE | CHARACTER | none | none | Julian data in YYDDD with YY being last two digits of the year, and DDD the Julian day of the year. |
General Parameters
| Card | Arguments | Default | Range | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WATER_DENSITY | REAL | none | none | Julian data in YYDDD with YY being last two digits of the year, and DDD the Julian day of the year. |
| WATER_TEMPERATURE | REAL | none | none | Julian hour . |
| DRYING_DEPTH | REAL | Calculated based on solution scheme and courant number | none | Sets to the time step for hydrodynamics in seconds. |
| SOLUTION_SCHEME | REAL | 48.0 | >RAMP>0 | Sets the duration of the model simulation in hours. |
| DURATION_RAMP | REAL | 1.0 | Sets the length of the ramp period in which the model forcing is slowly ramped from zero. |
Advanced Options
| Card | Arguments | Default | Range | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WATER_PONDING | CHARACTER | OFF | ON | OFF | Turns On or Off water ponding. If water ponding is Off, isolated bodies of water will become dry. |
| ONE_CELL_WIDE_CHANNELS | CHARACTER | ON | ON | OFF | Limits wetting and drying to areas with at least 3 cells wide. When turned off, the model stability is improved. |
| HYDRO_MAX_ITERATIONS | INTEGER | Function of grid size | >0 | Sets the maximum number of iterations for the flow (hydro) solver (outer loop). |
| PRESSURE_ITERATIONS | INTEGER | Depends on Solver | >0 | Sets the number of solver iterations for the pressure equation (inner loop). |
| VELOCITY_ITERATIONS | INTEGER | Depends on Solver | >0 | Sets the number of solver iterations for the velocity or momentum equations (inner loop). |
| MATRIX_SOLVER | CHARACTER | GMRES | GAUSS-SEIDEL | GAUSS-SEIDEL-SOR | BICGSTAB | GMRES | Selects the matrix solver for flow, sediment and salinity. |
| ADVECTION_SCHEME | CHARACTER | EXPONENTIAL | NONE | HYBRID | EXPONENTIAL | HLPA | Sets the advection scheme for flow, sediment and salinity. |