GenCade:Empirical Parameters: Difference between revisions
(Initial Creation) |
m (Update Figures) |
||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
[[File:D50Metric.png|500px|left]] [[File:D50Imperial.png|500px|right]] | [[File:D50Metric.png|500px|left]] [[File:D50Imperial.png|500px|right]] | ||
[[File:AValuesTable.png|700px|center]] | |||
Revision as of 17:11, 20 December 2022
Depth of Longshore Transport
The sand bypassing algorithm within GenCade requires a depth of active longshore transport, DLT, which is defined as the depth of breaking of the highest one tenth waves at the updrift side of the structure. Under standard assumptions, this depth is related to the significant wave height Hs (meters). This is used throughout as:
DLT = (1.27 / ɣ) Hb
where 1.27 is the conversion factor between the highest one-tenth wave height and the significant wave height. The depth of longshore transport is typically much less than the depth of closure, except under extreme wave conditions.
The characteristic maximum depth of longshore transport is DLTO is used to calculate the average beach slope (tanẞ, see Sand Transport Rates). It is calculated as introduced in Hallermeier (1983):
DLTO = 2.28HO - (10.9H2O / LO)
where HO is the significant wave height (meters) and LO is the wavelength (meters), both in deep water. In GenCade, DLTO is calculated at each time step using the deep water wave data, making the assumption that it is valid across the entire longshore extent of the modeled reach.
Average Profile and Shape
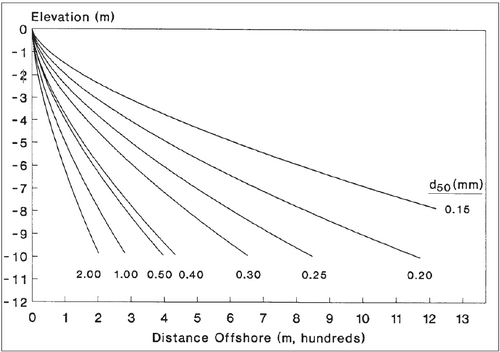
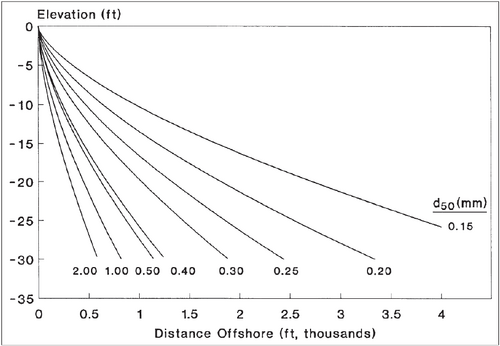
A profile shape must be specified to determine the location of the breaking waves alongshore and calculate the average nearshore bottom slope used in the longshore transport equation. Thus, the equilibrium profile shape introduced by Bruun (1954) and Dean (1977) is used as such:
D = Ay2/3
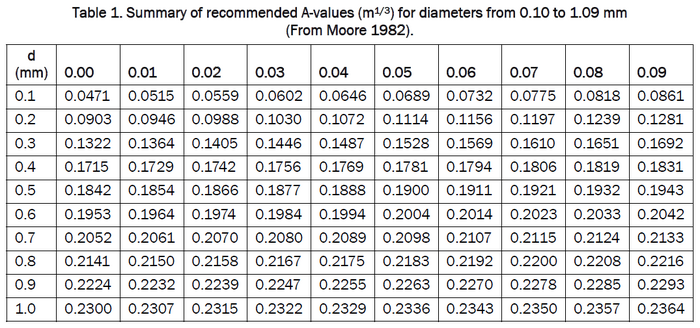
where D is the water depth (meters), y is the distance from the shoreline (meters), and A is the scale parameter (meters1/3). The scale parameter has been shown in Moore (1982) to depend on the median grain size (d50, in millimeters) which in turn effects the velocity (ws, in meters/second). This is due to the Kriebel et al. (1991) relation:
A = 2.25(w2s/g)1/3
If beach survey profiles for the target beach are available, it is recommended that the modeler use the curves in Figure 1 below (1a for metric units or 1b for American customary units) as templates to determine an 'effective' median grain size. The 'effective' grain size, if supplied to GenCade, will produce an A-value that will give the most representative profile shape. If profile survey data are lacking, the median grain size of the surf zone sand should be used. Table 1 is based on the methodology proposed in Moore (1982) and shows a summary of recommended A-values for grain size diameters.