CIRP April 2014 eNewsletter
Issue 34, April 2014
In this Newsletter:
CMS Technology Transfer for Great Lakes Districts through DOTS Program
Three separate training sessions on the Coastal Modeling System (CMS) were conducted on 3-6 Feb 2014 for the Buffalo District (LRB), 24-28 Feb 2014 for the Detroit District (LRE), and 7-11 Apr 2014 for the Chicago District (LRC). The training requests were initiated through the Dredging Operations Technical Support (DOTS) program. Dr. Zeki Demirbilek and Dr. Lihwa Lin, from CIRP, conducted training that was customized to the needs of District projects. These special-request trainings were closely coordinated with each District and customized for their specific needs. Modeling grids and inputs were prepared in advance based on review of project requirements and modeling capabilities pertinent to addressing specific needs of each project. Each hands-on training was tailored to each District project, with a focus on the technical features and capabilities of CMS-Wave and CMS-Flow models, as well as the models’ interface in the Surface-water Modeling System (SMS). Test simulations were performed and SMS, Fortran and Matlab tools were used to post-process and utilize modeling results in projects.
POC: (ERDC) Zeki Demirbilek, Zeki.Demirbilek@usace.army.mil
POC: (ERDC) Lihwa Lin, Lihwa.Lin@usace.army.mil
RSM and CIRP Nearshore Berms Working Meeting

The Regional Sediment Management (RSM) Program and Coastal Inlets Research Program (CIRP) teamed up to conduct a working meeting on placement of sediment in the nearshore, with support from the Dredging Operations and Environmental Research (DOER) Program. There were 52 participants from 13 Districts, ERDC-CHL, and ERDC-EL, with 21 participating via webinar. Sediment dredged from navigation channels often has a significant percentage (5-10% or more) of fines, which may be prohibited from direct placement on beaches by state law. Nearshore placement is a low-cost way of keeping sediment in the littoral system, providing a wave break that protects beaches, and allowing nature to sort fines offshore and transport coarser sand towards the beach. Topics discussed included environmental regulations and benefits; methods to determine the fate of berms, whether dispersive, stable, or migratory; guidance needed; existing models and tools that could be applied for calculations in the nearshore; and short- and long-term research needs. ERDC Team: Tanya Beck, Cheryl Pollock, Linda Lillycrop, and Julie Rosati.
POC: (ERDC) Tanya Beck, Tanya.M.Beck@usace.army.mil

The 2014 Navigation Research Area Review Group (RARG) Meeting was conducted from 1-3 April, 2014, in Vicksburg, MS. The CIRP presentation of 2014 R&D can be downloaded from the CIRP website under "Tech Transfer -> Meetings -> RARG2014." The RARG annually reviews research efforts and prioritizes statements of need (SoNs) submitted by non-ERDC USACE personnel through the Navigation Gateway (http://operations.usace.army.mil/navigation.cfm). Navigation RD&T program managers presented their work to date in an overview of the past year and identified work planned for this year and next. Fourteen SoNs submitted in the past year were presented and discussed, and previously unfunded SoNs were reviewed. The RARG had several technology transfer demonstrations during the first and second afternoons. CIRP's demonstration of WaveNet was given by Drs. Zeki Demirbilek and Derek Wilson, and the Automated Information System Analysis Package, AISAP, was demoed by Dr. Kenneth Ned Mitchell. At the end of the meeting, the RARG ranked the cumulative list of SoNs to identify priorities for new work to begin in FY15 (rankings to be announced).
POC: (ERDC) Julie Rosati, Julie.D.Rosati@usace.army.mil
Kikiaola Harbor, HI Infrastructure Modifications Study
The Honolulu District (POH) and ERDC are evaluating alternatives to improve navigation in the entrance and interior of the Kikiaola Light Draft Harbor (KLDH), a small boat harbor located on the southwest coast of Kauai Island, Hawaii. The study includes field data collection and monitoring, and numerical wave modeling for evaluation of the structural alternatives for federal modification of KLDH. The entrance and interior of KLDH is affected by high-energy northwest swells, southern swells and storms transforming over a wide shallow reef, causing unfavorable navigation conditions for boats using this harbor. A six-month field data collection study provided wave data for calibration of numerical models at five gauges, two outside and three inside the harbor. Detailed surveys of bathymetry and structures were conducted to obtain data for numerical modeling. BOUSS-2D and CMS-Wave models were used in this infrastructure modifications modeling study, and evaluation and ranking of the eight alternatives for reducing waves in the interior harbor and entrance and access channel. The study has been completed, and final draft report is being evaluated by POH.
POC: (ERDC) Zeki Demirbilek, Zeki.Demirbilek@usace.army.mil
POC: (ERDC) Lihwa Lin, Lihwa.Lin@usace.army.mil
POC: (ERDC) William Butler, William.Butler@usace.army.mil
POC: (ERDC) Kent Hathaway, Kent.K.Hathaway@usace.army.mil
POC: (POH) Tom Smith, Thomas.D.Smith@usace.army.mil
POC: (POH) Jessica Podoski, Jessica.H.Podoski@usace.army.mil
Wave, Hydrodynamic & Morphologic Modeling in Support of the Lateral Expansion of Poplar Island, MD
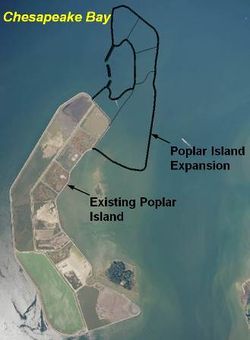
CIRP and the Baltimore District (NAB) are conducting a wave, hydrodynamic, and particle tracking modeling study in support of the Baltimore District’s design analysis for the lateral expansion of Poplar Island. The island expansion implements the use of an embayment, which must be optimized to minimize sedimentation and reduce the wave climate, and results in a technically sound design for a series of dike/breakwaters across the mouth of embayment. This study will include determining the hydrodynamic, wave, and wind forcing conditions, and modeling different breakwater alternatives to examine sediment dynamics, wave climate and hydrodynamic regimes within the embayment for each alternative. The CIRP will run ADCIRC and CMS to obtain regional scale wind and waves. The CMS/PTM will be used to calculate wave height/energy, flow, and particle movement for the alternatives. The final results will show changes in waves and current within the embayment and sediment particle behavior corresponding to different dike/breakwater configurations, and will determine the most favorable alternative.
POC: (ERDC) Honghai Li, Honghai.Li@usace.army.mil
POC: (ERDC) Tanya Beck, Tanya.M.Beck@usace.army.mil
POC: (ERDC) Mitchell Brown, Mitchell.E.Brown@usace.army.mil
POC: (NAB) Tom Laczo, Thomas.D.Laczo@usace.army.mil
POC: (NAB) Tom Myrah, Thomas.P.Myrah@usace.army.mil
Change in Newsletter Frequency
Our eNewsletter is transitioning to bi-annual eNewletters. We will provide updates on CIRP R&D each April and October, immediately after our annual RARG and at the start of the Fiscal Year. However, we always invite input from inlet interests!
POC: (ERDC) Julie Rosati, Julie.D.Rosati@usace.army.mil
Engineer Research & Development Center
3909 Halls Ferry Road, Coastal & Hydraulics Laboratory
Vicksburg, MS 39180
251-635-9519