CMS-Flow Model Parameters: Difference between revisions
| Line 94: | Line 94: | ||
=== Parameters === | === Parameters === | ||
=== [https://cirpwiki.info/wiki/Bottom_Friction Bottom Friction] === | === [https://cirpwiki.info/wiki/Bottom_Friction Bottom Friction] === | ||
====Parameters==== | |||
[[File:CMSFlow Model Parameters GeneralTab Flow Parameters V13.2.12.png|500px|thumb|right|CMS Flow Paramterers Version 13.2.12]] | |||
*Hydrodynamic Time Step | |||
*[https://cirpwiki.info/wiki/CMS-Flow_NUmerical_Methods:_Wetting_and_Drying Wetting and Drying] | |||
====Bottom and wall friction==== | |||
====Turbulance parameters===== | |||
====Edit turbulence parameters==== | |||
====Write recurring hot start file==== | |||
=== Turbulence parameters === | === Turbulence parameters === | ||
Revision as of 19:54, 12 December 2022
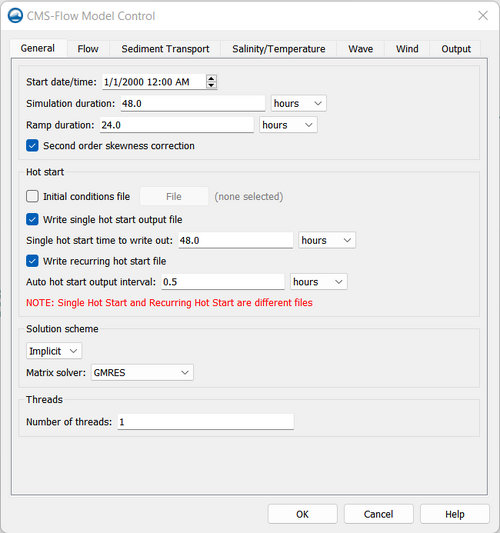
All of the CMS-Flow model parameters, settings, and output options are controlled from the CMS-Flow Model Control window (Figure 1). The window has several tabs including the Flow tab in which most of the general settings are set for CMS-Flow. To open the CMS-Flow Model Control window, click on CMS-Flow | Model Control. The first tab will be the Flow tab. There are several sections within the tab including Time Control and Hot Start options.
General
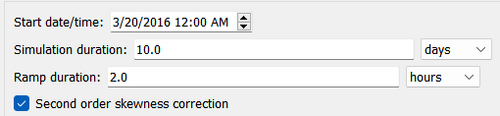
Time Control
Below are some of the CMS cards related to the Time Control of the Flow tab. Table 1 provides a brief description of the CMS cards used for time control.
| Card | Arguments | Default | Range | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| STARTING_JDATE | REAL | none | none | Julian data in YYDDD with YY being last two digits of the year, and DDD the Julian day of the year. |
| STARTING_JDATE_HOUR | REAL | none | none | Julian hour . |
| HYDRO_TIME_STEP | REAL | Calculated based on solution scheme and courant number | none | Sets to the time step for hydrodynamics in seconds. |
| DURATION_RUN | REAL | 48.0 | >RAMP>0 | Sets the duration of the model simulation in hours. |
| DURATION_RAMP | REAL | 1.0 | Sets the length of the ramp period in which the model forcing is slowly ramped from zero. |
Hot Start
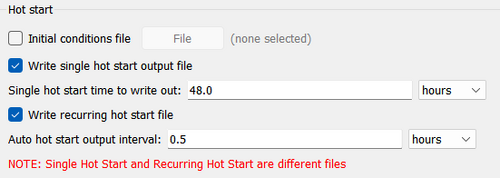
The term Hot start refers to starting a simulation with an initial condition other zero (cold start). Hot starts are used for specifying initial conditions or restarting simulations at intermediate times. The hot start controls are set in the Flow tab of the CMS-Flow Model Control window.
Hot Start File
The CMS hot start feature CMS lets the user restart simulations that have been stopped due to electric outages, hardware malfunctions, or model crashes. In the case of a model crash the user, may restart the model using larger solver iterations and/or time steps to stabilize the simulation. The user has the option to specify a hot start output time or an interval for outputting a recurring hot start file. Every time the hot start file is written, it overwrites the previous information. The CMS Hot Start file saves information on the water elevation (pressure), and current velocities. If the sediment transport is active, then the water depth and sediment concentrations are also saved for each size class. Only the very last record of information is preserved (no starting from earlier intervals).
The CMS hot start files are written as binary XMDF files by default. Depending on the type of hot start (single file or recurring), the names are as follows are saved in the directory of the CMS-Flow files:
- SingleHotStart.h5
- AutoHotStart.h5
After saving a CMS Hot Start file, it is a good idea to rename the file with a different name before using it as an initial conditions file. This way, the file will not be overwritten in future simulations.
Table 1. Hot Start CMS-Flow Cards
| Card | Arguments | Default | Range | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HOT_START_TIME | REAL | none | none | Single time after start at which to output a single hot start file. |
| AUTO_HOT_START_INTERVAL | REAL | none | none | Sets the recurring hot start output interval . |
- Initial conditions file
- Write Hot Start output file
- Automatic recurring Hot Start file
Solution Scheme
This refers to the temporal discretization of the hydrodynamic, sediment and salinity transport equations. There are two options in CMS:
- Implicit - First order backward Euler scheme. Uses a time step on the order of 5-15 minutes. Appropriate for cases which can be simulated with large computational time steps such as long term morphology change at inlets.
- Explicit - First order forward Euler scheme. Uses a time step on the order of 0.5-1.0 second. Appropriate for cases that vary quickly in time such as flooding or barrier island breaching.
Matrix Solver
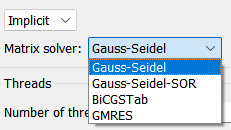
Users have a matrix solver:
| Card | Arguments | Default | Range | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SOLUTION_SCHEME | CHARACTER | EXPLICIT | EXPLICIT | IMPLICIT | Determines the solution scheme used in CMS-Flow. |
Threads
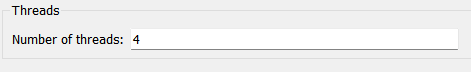
- Number of threads
The CMS-Flow is parallelized for PC’s with multi-core processors using OpenMP. The parallelization works by splitting the computational work into “threads” among several cores. Some cores are hyper-threaded, meaning a single core may support two threads. The number of threads is specified in the CMS-Flow Model Control Window. The number of threads must be equal or greater to 1 and cannot be larger than the number of threads available on the machine. If a number is specified which is larger than the maximum number available on the machine, then the code will default to the maximum number available.
Table 2-102. CMS-Flow card used to specify the number of threads.
| Input | Format | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Number of computing threads | [cards=NUM_THREADS]
[name=NumThr, type=int, range=(NumThr>=1), default=1] |
Determines the number of threads used for parallel processing. |
For more detail, see Multi Processor Capability
Reference: CMS User Guide 013
Flow
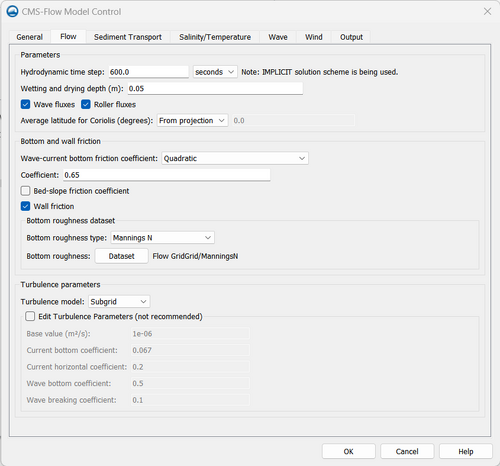
Parameters
Bottom Friction
Parameters
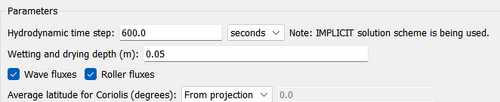
- Hydrodynamic Time Step
Bottom and wall friction
Turbulance parameters=
Edit turbulence parameters
Write recurring hot start file
Turbulence parameters
Sediment Transport
Timing
Formulation
Transport formula
Properties
Bed Composition
Scaling factors and coefficients
Adaptation
Transport grain sizes classes
Avalanching
Hard Bottom
Salinity/Temperature
The general parameters are the water density and temperature. The CMS-Flow cards for the general parameters are described in the table below.
Table 1. CMS-Flow cards related to the general parameters
| Card | Arguments | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| WATER_DENSITY | REAL | 1025 | Water density in kg/m^3. |
| WATER_TEMPERATURE | REAL | 15 | Water temperature in degrees Celcius. |
Wave
Wind
Output