CMS: Difference between revisions
| Line 43: | Line 43: | ||
---- | ---- | ||
*'''Hydrodynamics''' | *'''Hydrodynamics''' | ||
**[[CMS-Flow Hydrodnamics: Variable_Definitions|Variable_Definitions]] | |||
**[[CMS-Flow:Hydro_Eqs|Governing Equations]] | **[[CMS-Flow:Hydro_Eqs|Governing Equations]] | ||
**[[CMS-Flow:Bottom_Friction|Bed Shear Stresses]] | **[[CMS-Flow:Bottom_Friction|Bed Shear Stresses]] | ||
Revision as of 19:08, 28 July 2014
__notitle__
Coastal Modeling System
An Advanced Engineering Tool
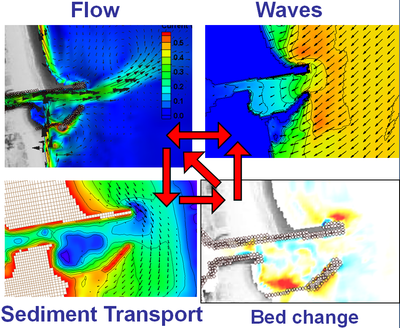
The Coastal Modeling System is an integrated suite of numerical models for simulating flow, waves, sediment transport, and morphology change in coastal areas. The system is designed for practical applications in navigation channel performance and sediment management for coastal inlets and adjacent beaches in order to improve the usage of USACE Operation and Maintenance Funds. The CMS is intended as a research and engineering tool that can be used on desk-top computers. The CMS takes advantage of the Surface-water Modeling System (SMS) interface for grid generation and model setup, as well as plotting and post-processing.
- Background
The CMS has been a research and development area of the Coastal Inlets Research Program (CIRP) at the United States Army Corps of Engineers - Engineering Research and Development Center (USACE-ERDC), Coastal and Hydraulics Laboratory (CHL) since 2006. It was built from a group of numerical models that have been under development since 2002. Information on the CIRP and publications on the CMS can be found at the CIRP Website.
- Key Features
- Fully integrated system
- Finite Volume Method - Mass conservative
- Non-uniform Cartesian Grid - Easy to setup and run
- Telescoping Cartesian Grid - Flexible, efficient, and easier to generate than unstructured meshes
- Supports most common types of forcing and boundary conditions
- Robust numerical schemes for reliable, crash-free simulations
- Parallelization on desktop computers for fast computation
- User-friendly interface
System Components

CMS-Flow is a coupled hydrodynamic and sediment transport model capable of simating depth-averaged circulation, salinity and sediment transport due to tides, wind and waves. The hydrodynamic model sovles the conservative form of the shallow water equations and includes terms for the Coriolis force, wind stress, wave stress, bottom stress, vegetation flow drag, bottom and friction, and turbulent diffusion. There are three sediment transport models available in CMS: a sediment mass balance model, an equilibrium advection diffusion model, and non-equilibrium advection-diffusion model. The salinity transport is simulated with the standard advection diffusion model and includes evaporation and precipitaion. All equations are solved using the Finite Volume Method on a non-uniform Cartesian grid. For additional information on CMS-Flow visit CMS-Flow Main Page.
The CMS-Wave is a spectral wave transformation model and solves the steady-state wave-action balance equation on a non-uniform Cartesian grid. It considers wind wave generation and growth, diffraction, reflection, dissipation due to bottom friction, whitecapping and breaking, wave-wave and wave-current interactions, wave runup, wave setup, and wave transmission through structures. For additional information information on CMS-Wave visit CMS-Wave Main Page.
Documentation Portal
Technical Documentation
|
User GuideCMS-Flow
CMS-Wave |
Examples, applications and moreWorkshops Downloads
|
External Links:
- US Army Engineer Research and Development Center - Ongoing Research [1]
- Presentations (MVN Workshop - June 2009)
- Aug 2008 Two-Dimensional Depth-Averaged Circulation Model CMS-M2D: Version 3.0, Report 2, Sediment Transport and Morphology Change [7]
{{#rawmsg:back}}